Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain Boyle's Law on the basis of the kinetic theory of matter.
उत्तर
Boyle's law on the basis of the kinetic theory of matter:
- According to the kinetic theory of matter, the number of particles present in a given mass and the average kinetic energy is constant.
- If the volume of the given mass of a gas is reduced to half of its original volume, then the same number of particles will have half the space to move.
- As a result, the number of molecules striking the unit area of the walls of the container at a given time will double and the pressure will also double.
- Alternatively, if the volume of a given mass of a gas is doubled at a constant temperature, the same number of molecules will have double the space to move.
- Thus, the number of molecules striking the unit area of the walls of a container at a given time will become one-half of the original value.
- Thus, the pressure will also get reduced to half of the original pressure. Hence, it is seen that if the pressure increases, the volume of a gas decreases at a constant temperature, which is Boyle's law.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
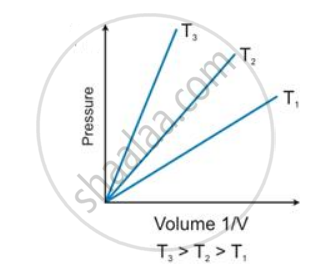
State the law which is represented by the following graph:
A steel cylinder of internal volume 20 litres is filled with hydrogen at 29 atmospheric pressure. If hydrogen is used to fill a balloon at 1.25 atmospheric pressure at the same temperature, what volume will the gas occupy?
Correct the following statement:
The volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at a constant temperature.
50 cm3 of hydrogen is collected over water at 17°C and 750 mmHg pressure. Calculate the volume of a dry gas at STP. The water vapour pressure at 17°C is 14 mmHg.
A given mass of a gas occupied 143 cm3 at 27° C and 700 mm Hg pressure. What will be its volume at 300 K and 280 mm Hg pressure?
A gas cylinder having a capacity of 20 litres contains a gas at 100 atmos. How many flasks of 200 cm3 capacity can be filled from it at 1 atmos. pressure if the temperature remains constant?
Name or state the following:
The law which studies the relationship between pressure of a gas and the volume occupied by it at constant temperature.
Assuming temperature remaining constant calculate the pressure of the gas in the following:
The pressure of a gas having volume 1800 ml. originally occupying 300 ml. at 6 atms. pressure.
According to Boyle’s law, the shape of the graph between pressure and reciprocal of volume is _______.
The following question refers to one mole of chlorine gas.
What will happen to volume of gas, if pressure is doubled?
