Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Give its
(i) mathematical expression
(ii) graphical representation and
(iii) significance.
उत्तर
(i) mathematical expression
suppose a gas occupies volume V1 when its pressure is P1; then
`"V"_1 ∝ 1/"P"_1 "or" "V"_1 = "k"/"P"_1`
`"P"_1"V"_1 = "k" = "constant"`
If V2 is the volume ocuupied when the pressure is P2 at the same temperature, the
`"V"_2 ∝ 1/"P"_2 "or" "V"_2 = "k"/"P"_2`
`"P"_2"V"_2 = "k" = "constant"`
`"P"_1"V"_1 = "P"_2"V"_2 = "k"` at constant temperature.
This is called Boyle's law equation.
(ii) graphical representation
The law can be verified by plotting a graph
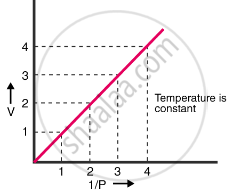
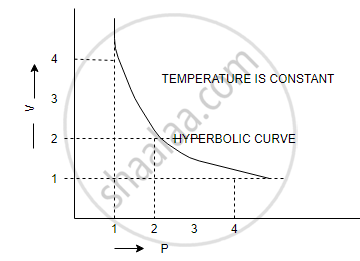
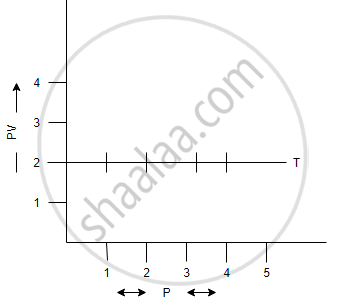
(a) V vs `1/p` (b) V vs P (c) PV vs P
(a) V vs `1/p`: a straight line passing through the origin is obtained
(b) V vs P: a hyperbolic curve in the first quadrant is obtained
(c) PV vs P: a straight line is obtained parallel to the pressure axis.
(iii) Significance
On increasing pressure, volume decreases. The gas becomes denser. Thus at a constant temperature, the density of a gas is directly proportional to its pressure.
Atmospheric pressure is low at high altitudes, so air is less dense. Hence, a lesser quantity of oxygen is available for breathing. This is the reason why mountaineers have to carry oxygen cylinders with them.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct answer:
If the pressure is doubled for a fixed mass of a gas, its volume will become
At constant temperature, the effect of change of pressure on the volume of a gas was as given below:
|
Pressure in atmosphere |
Volume in liters |
|
0.20 |
112 |
|
0.25 |
89.2 |
|
0.40 |
56.25 |
|
0.60 |
37.40 |
|
0.80 |
28.10 |
|
1.00 |
22.4 |
(a) Plot the following graphs
- P vs V
- P vs 1/V
- PV vs P
Interpret each graph in terms of the law.
(b) Assuming that the pressure values given above are correct, find the correct measurement of the volume.
A gas at 240 K is heated to 127°C. Find the percentage change in the volume of the gas (pressure remaining constant).
At 0°C and 760 mmHg pressure, a gas occupies a volume of 100 cm3. Kelvin temperature of the gas is increased by one-fifth and the pressure is increased one and a half times. Calculate the final volume of the gas.
A certain mass of a gas occupies 2 litres at 27°C and 100 Pa. Find the temperature when volume and pressure become half of their initial values.
50 cm3 of hydrogen is collected over water at 17°C and 750 mmHg pressure. Calculate the volume of a dry gas at STP. The water vapour pressure at 17°C is 14 mmHg.
A given mass of a gas occupied 143 cm3 at 27° C and 700 mm Hg pressure. What will be its volume at 300 K and 280 mm Hg pressure?
Calculate the following:
A gas ‘X’ is collected over water at 17°C and 750 mm. pressure. If the volume of the gas collected is 50 cc., calculate the volume of the dry gas at s.t.p. [at 17°C the vapour pressure is 14 mm.]
Fill in the blank with the correct word, from the words in option:
1 dm3 of a gas is equal to _______.
According to Boyle’s law, the shape of the graph between pressure and reciprocal of volume is _______.
