Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain briefly with the help of necessary diagrams, the forward biasing of a p-n junction diode. Also draw characteristic curves.
उत्तर
p-n junction diode under forward bias

p-side is connected to positive terminal and n-side to the negative terminal.
Applied voltage drops across the depletion region.
Direction of applied voltage (V) is opposite to the build in potential (V0).
As the depletion layer width decreases, the barrier height is reduced.
Effective barrier height under forward bias is (V0 − V).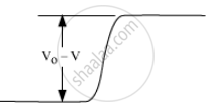
-
Electron in n-region moves towards the p-n junction and holes in p-region move towards the junction. The width of the depletion layer decreases and hence, it offers less resistance.
-
Diffusion of majority carriers takes place across the junction.
This leads to forward current.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A student wants to use two p-n junction diodes to convert alternating current into direct current. Draw the labelled circuit diagram she would use and explain how it works.
When a p-type impurity is doped in a semiconductor, a large number of holes are created, This does not make the semiconductor charged. But when holes diffuse from the p-side to the n-side in a p-n junction, the n-side gets positively charged. Explain.
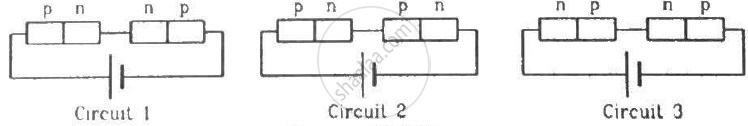
Two identical p-n junction may be connected in series with a battery in three ways. The potential difference across the two p-n junctions are equal in
A hole diffuses from the p-side to the n-side in a p-n junction. This means that
The current−voltage characteristic of an ideal p-n junction diode is given by \[i = i_0 ( e^{eV/KT} - 1)\] where, the drift current i0 equals 10 µA. Take the temperature T to be 300 K. (a) Find the voltage V0 for which \[e^{eV/kT} = 100 .\]One can neglect the term 1 for voltages greater than this value. (b) Find an expression for the dynamic resistance of the diode as a function of V for V > V0. (c) Find the voltage for which the dynamic resistance is 0.2 Ω.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
What are the readings of the ammeters A1 and A2 shown in figure. Neglect the resistance of the meters.
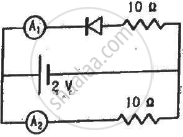
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Find the current through the battery in each of the circuits shown in figure.
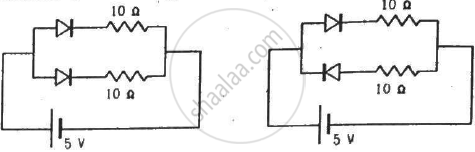
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
Find the current through the resistance R in figure if (a) R = 12Ω (b) R = 48Ω.
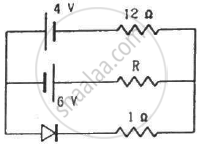
(Assume that the resistance of each diode is zero in forward bias and is infinity in reverse bias.)
When the base current in a transistor is changed from 30µA to 80µA, the collector current is changed from 1.0 mA to 3.5 mA. Find the current gain β.
Zener breakdown occurs in a p-n junction having p and n both:
