Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the construction of plane wavefront using Huygens’ principle.
उत्तर

a. A plane wavefront is formed when point of observation is very far away from the primary source.
b. Let PQR represent a plane wavefront at any instant. According to Huygens’ principle,all the points on this wavefront will act as secondary sources of light sending out secondary wavelets in the forward direction.
c. Draw hemispheres with P, Q, R…. as centres and ‘ct’ as radius. The surface tangential
to all such hemispheres is P1Q1R1…. at instant ‘t’. It is a new wavefront at time ‘t’.
d. The plane wavefronts is propagated as plane waves in homogeneous isotropic medium.They are parallel to each other.
e. PP1N1, QQ1N2, RR1N3 are the wave normals at P, Q, R respectively. These wave normals show the direction of propagation of plane wavefront.
f. The new wavefront P1Q1R1 is parallel to primary wavefront PQR.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Using Huygens's construction of secondary wavelets explain how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a narrow slit on which a monochromatic beam of light is incident normally.
What is the shape of the wavefront in the following case?
Light emerging out of a convex lens when a point source is placed at its focus.
State Huygen's principle.
Use Huygens' principle to verify the laws of refraction.
The refractive indices of water and diamond are `4/3` and 2.42 respectively. Find the speed of light in water and diamond. (c = 3x108 m/s)
Using Huygens’ principle, verify the laws of reflection at a plane surface.
Using this principle draw a diagram to show how a plane wave front incident at the interface of the two media gets refracted when it propagates from a rarer to a denser medium. Hence verify Snell's law of refraction.
State Huygens’s principle. Show, with the help of a suitable diagram, how this principle is used to obtain the diffraction pattern by a single slit.
Draw a plot of intensity distribution and explain clearly why the secondary maxima becomes weaker with increasing order (n) of the secondary maxima.
Huygens' principle of secondary wavelets may be used to
(a) find the velocity of light in vacuum
(b) explain the particle behaviour of light
(c) find the new position of a wavefront
(d) explain Snell's Law
Define the term 'wavefront of light'. A plane wavefront AB propagating from a denser medium (1) into a rarer medium (2) is incident of the surface P1P2 separating the two media as shown in fig.
Using Huygen's principle, draw the secondary wavelets and obtain the refracted wavefront in the diagram.
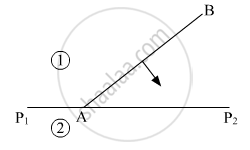
According to Huygen's construction, relation between old and new wavefront is ______.
What is the phase difference between any two points lying on the same?
The inverse square law of intensity is valid for a
Wavefront means
Huygen's conception of secondary waves ______.
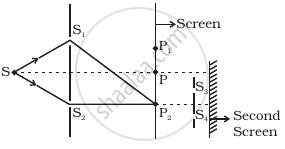
Figure shows a standard two slit arrangement with slits S1, S2, P1, P2 are the two minima points on either side of P (Figure). At P2 on the screen, there is a hole and behind P2 is a second 2-slit arrangement with slits S3, S4 and a second screen behind them.
For light diverging from a point source ______.
- the wavefront is spherical.
- the intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared.
- the wavefront is parabolic.
- the intensity at the wavefront does not depend on the distance.
Is Huygen’s principle valid for longitudinal sound waves?
What is the shape of the wavefront on earth for sunlight?
Two light beams of intensities in the ratio of 9 : 4 are allowed to interfere. The ratio of the intensity of maxima and minima ______.
According to Huygens's principle, the amplitude of secondary wavelets is ______.
What type of wavefronts are associated with a source infinity?
Represent diagrammatically how the incident planar wavefronts of wavelength λ pass through an aperture of size d, when d is approximately equal to λ.
Represent diagrammatically how the incident planar wavefronts of wavelength λ pass through an aperture of size d, when d is approximately equal to λ.
