Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Using this principle draw a diagram to show how a plane wave front incident at the interface of the two media gets refracted when it propagates from a rarer to a denser medium. Hence verify Snell's law of refraction.
उत्तर
Huygens’ Principle:
• Each point on the primary wave front acts as a source of secondary wavelets, sending out disturbance in all directions in a similar manner as the original source of light does.
• The new position of the wave front at any instant (called secondary wave front) is the envelope of the secondary wavelets at that instant.
Refraction On The Basis Of Wave Theory
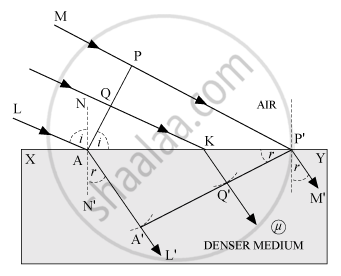
• Consider any point Q on the incident wave front.
• Suppose when disturbance from point P on incident wave front reaches point P'on the refracted wave front, the disturbance from point Q reaches Q' on the refracting surface XY.
• Since P'A'epresents the refracted wave front, the time taken by light to travel from a point on incident wave front to the corresponding point on refracted wave front should always be the same. Now, time taken by light to go from Q to Q' will be `t = (QK)/c + (KQ)/v ...(1)`
In right-angled ΔAQK, ∠QAK = i
∴ QK = AK sin i … (2)
In right-angled ΔP'Q'K, ∠Q'P'K, = r and KQ = KP sin r…. (3)
Substituting (2) and (3) in equation (1),
`t = (AK sin i)/c + (KP'sin r)/v`
or, `(AK sin i)/c + ((AP' - AK)sin r)/v` (∵ KP' = AP' -AK)
or,`t = (AP')/c sinr + AK ((sin i )/c - (sin r)/v) ...... (4)`
The rays from different points on the incident wave front will take the same time to reach the corresponding points on the refracted wave front i.e., t given by equation (iv) is independent of AK. It will happen so, if`(sin i)/c -(sin r)/v =0 ⇒ (sini)/(sinr) =c/v ⇒μ = (sini)/(sinr) `
This is the Snell’s law for refraction of light.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the shape of the wavefront in the following case?
The portion of the wavefront of light from a distant star was intercepted by the Earth.
You have learnt in the text how Huygens’ principle leads to the laws of reflection and refraction. Use the same principle to deduce directly that a point object placed in front of a plane mirror produces a virtual image whose distance from the mirror is equal to the object distance from the mirror.
The refractive indices of water and diamond are `4/3` and 2.42 respectively. Find the speed of light in water and diamond. (c = 3x108 m/s)
Light waves travel in vacuum along the X-axis. Which of the following may represent the wave fronts?
According to Huygen's construction, relation between old and new wavefront is ______.
Huygen's conception of secondary waves ______.
Is Huygen’s principle valid for longitudinal sound waves?
According to Huygens's principle, the amplitude of secondary wavelets is ______.
Using Huygen's wave theory of light, show that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
Represent diagrammatically how the incident planar wavefronts of wavelength λ pass through an aperture of size d, when d is approximately equal to λ.
