Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Light waves travel in vacuum along the X-axis. Which of the following may represent the wave fronts?
पर्याय
x = c
y = c
z = c
x + y + z = c
उत्तर
x = c
The wave is travelling along the X-axis. So, it'll have planar wavefront perpendicular to the X-axis.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
On the basis of Huygens' wave theory of light prove that velocity of light in a rarer medium is greater than velocity of light in a denser medium.
Using Huygens's construction of secondary wavelets explain how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a narrow slit on which a monochromatic beam of light is incident normally.
What is the shape of the wavefront in the following case?
The portion of the wavefront of light from a distant star was intercepted by the Earth.
State Huygen's principle.
Consider a plane wave front incident on a thin convex lens. Draw a proper diagram to show how the incident wave front traverses through the lens and after refraction focusses on the focal point of the lens, giving the shape of the emergent wave front.
Using this principle draw a diagram to show how a plane wave front incident at the interface of the two media gets refracted when it propagates from a rarer to a denser medium. Hence verify Snell's law of refraction.
When the width of the slit is made double the original width, how would this affect the size and intensity of the central diffraction band?
State Huygens’s principle. Show, with the help of a suitable diagram, how this principle is used to obtain the diffraction pattern by a single slit.
Draw a plot of intensity distribution and explain clearly why the secondary maxima becomes weaker with increasing order (n) of the secondary maxima.
Derive the law of reflection using Huygen’s Wave Theory.
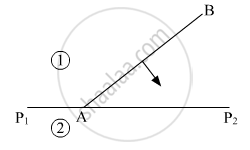
Define the term 'wavefront of light'. A plane wavefront AB propagating from a denser medium (1) into a rarer medium (2) is incident of the surface P1P2 separating the two media as shown in fig.
Using Huygen's principle, draw the secondary wavelets and obtain the refracted wavefront in the diagram.
Relation between ray and wavefront is ______.
What is the phase difference between any two points lying on the same?
The inverse square law of intensity is valid for a
For light diverging from a point source ______.
- the wavefront is spherical.
- the intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared.
- the wavefront is parabolic.
- the intensity at the wavefront does not depend on the distance.
What is the shape of the wavefront on earth for sunlight?
How is a wavefront different from a ray?
Represent diagrammatically how the incident planar wavefronts of wavelength λ pass through an aperture of size d, when d is approximately equal to λ.
