Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider a plane wave front incident on a thin convex lens. Draw a proper diagram to show how the incident wave front traverses through the lens and after refraction focusses on the focal point of the lens, giving the shape of the emergent wave front.
उत्तर
The new position of the wavefront at any instant (called secondary wave front) is the envelope of the secondary wavelets at that instant.
Incident wave front traversing through the lens and after refraction focusing on the focal point of the lens is shown in the figure below.
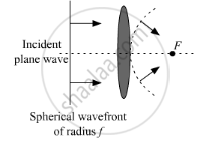
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the construction of plane wavefront using Huygens’ principle.
What is the shape of the wavefront in the following case?
Light emerging out of a convex lens when a point source is placed at its focus.
The refractive indices of water and diamond are `4/3` and 2.42 respectively. Find the speed of light in water and diamond. (c = 3x108 m/s)
Using this principle draw a diagram to show how a plane wave front incident at the interface of the two media gets refracted when it propagates from a rarer to a denser medium. Hence verify Snell's law of refraction.
With what type of source of light are cylindrical wave fronts associated?
Define a wavefront. Using 'Huygens' principle, draw the shape of a refracted wavefront, when a plane wave is incident on a convex lens.
The inverse square law of intensity is valid for a
For light diverging from a point source ______.
- the wavefront is spherical.
- the intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared.
- the wavefront is parabolic.
- the intensity at the wavefront does not depend on the distance.
According to Huygens's principle, the amplitude of secondary wavelets is ______.
Using Huygen's wave theory of light, show that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
