Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the constant b that makes g continuous on `(- oo, oo)`.
`g(x) = {{:(x^2 - "b"^2,"if" x < 4),("b"x + 20, "if" x ≥ 4):}`
उत्तर
`g(x) = {{:(x^2 - "b"^2,"if" x < 4),("b"x + 20, "if" x ≥ 4):}`
Given g is continuous on R.
∴ g(x) is continuous at x = 4.
`lim_(x -> 4^-) g(x) = lim_(x -> 4^+) g(x)`
`lim_(x ->4^-) (x^2 - "b"^2) = lim_(x -> 4^+) ("b"x + 20)`
42 – b2 = b × 4 + 20
16 – b2 = 4b + 20
b2 + 4b + 20 – 16 = 0
b2 + 4b + 4 = 0
(b + 2)2 = 0
b + 2 = 0 ⇒ b = – 2
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Prove that f(x) = 2x2 + 3x - 5 is continuous at all points in R
Examine the continuity of the following:
ex tan x
Examine the continuity of the following:
x . log x
Examine the continuity of the following:
`sinx/x^2`
Examine the continuity of the following:
|x + 2| + |x – 1|
Examine the continuity of the following:
`|x - 2|/|x + 1|`
Examine the continuity of the following:
cot x + tan x
Let `f(x) = {{:(0",", "if" x < 0),(x^2",", "if" 0 ≤ x ≤ 2),(4",", "if" x ≥ 2):}`. Graph the function. Show that f(x) continuous on `(- oo, oo)`
If f and g are continuous functions with f(3) = 5 and `lim_(x -> 3) [2f(x) - g(x)]` = 4, find g(3)
Find the points at which f is discontinuous. At which of these points f is continuous from the right, from the left, or neither? Sketch the graph of f.
`f(x) = {{:(2x + 1",", "if" x ≤ - 1),(3x",", "if" - 1 < x < 1),(2x - 1",", "if" x ≥ 1):}`
Which of the following functions f has a removable discontinuity at x = x0? If the discontinuity is removable, find a function g that agrees with f for x ≠ x0 and is continuous on R.
`f(x) = (x^2 - 2x - 8)/(x + 2), x_0` = – 2
Consider the function `f(x) = x sin pi/x`. What value must we give f(0) in order to make the function continuous everywhere?
State how continuity is destroyed at x = x0 for the following graphs.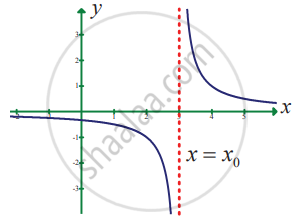
State how continuity is destroyed at x = x0 for the following graphs.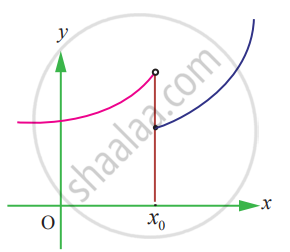
Choose the correct alternative:
Let f be a continuous function on [2, 5]. If f takes only rational values for all x and f(3) = 12, then f(4.5) is equal to
Choose the correct alternative:
Let a function f be defined by `f(x) = (x - |x|)/x` for x ≠ 0 and f(0) = 2. Then f is
