Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A transformer is designed to convert an AC voltage of 220 V to an AC voltage of 12 V. If the input terminals are connected to a DC voltage of 220 V, the transformer usually burns. Explain.
उत्तर
A transformer is ideally an inductive coil. For an inductor connected across a DC voltage,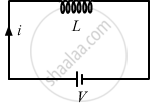
`V - L (di)/(dt) = 0`
`⇒ V = L(di)/(dt)`
⇒ \[\int\limits\] `di = V/L` \[\int\limits\] dt
`⇒ i = (Vt)/L`
For a DC source, the current across the inductor will increase with time and can reach a very large value, which can burn the transformer.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A current i1 = i0 sin ωt passes through a resistor of resistance R. How much thermal energy is produced in one time period? A current i2 = −i0 sin ωt passes through the resistor. How much thermal energy is produced in one time period? If i1 and i2 both pass through the resistor simultaneously, how much thermal energy is produced? Is the principle of superposition obeyed in this case?
Is energy produced when a transformer steps up the voltage?
An AC source producing emf ε = ε0 [cos (100 π s−1)t + cos (500 π s−1)t] is connected in series with a capacitor and a resistor. The steady-state current in the circuit is found to be i = i1 cos [(100 π s−1)t + φ1) + i2 cos [(500π s−1)t + ϕ2]. So,
A bulb rated 60 W at 220 V is connected across a household supply of alternating voltage of 220 V. Calculate the maximum instantaneous current through the filament.
Compare resistance and reactance.
A device Y is connected across an AC source of emf e = e0 sin ωt. The current through Y is given as i = i0 sin (ωt + π/2).
- Identify the device Y and write the expression for its reactance.
- Draw graphs showing a variation of emf and current with time over one cycle of AC for Y.
- How does the reactance of the device Y vary with the frequency of the AC? Show graphically.
- Draw the phasor diagram for device Y.
Suppose the initial charge on the capacitor is 6 mC. What is the total energy stored in the circuit initially? What is the total energy at later time?
Average power supplied to a capacitor over one complete cycle is ______.
If circuit containing capacitance only, the current ______.
A capacitor has capacitance C and reactance X, if capacitance and frequency become double, then reactance will be ______.
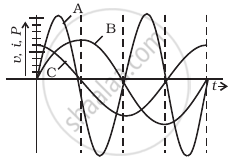
A device ‘X’ is connected to an a.c source. The variation of voltage, current and power in one complete cycle is shown in figure.
- Which curve shows power consumption over a full cycle?
- What is the average power consumption over a cycle?
- Identify the device ‘X’.
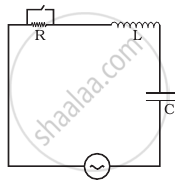
In the LCR circuit shown in figure, the ac driving voltage is v = vm sin ωt.
- Write down the equation of motion for q (t).
- At t = t0, the voltage source stops and R is short circuited. Now write down how much energy is stored in each of L and C.
- Describe subsequent motion of charges.
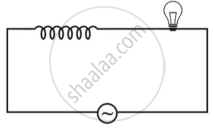
An iron cored coil is connected in series with an electric bulb with an AC source as shown in figure. When iron piece is taken out of the coil, the brightness of the bulb will ______.
A resistor of 50 Ω, a capacitor of `(25/pi)` µF and an inductor of `(4/pi)` H are connected in series across an ac source whose voltage (in volts) is given by V = 70 sin (100 πt). Calculate:
- the net reactance of the circuit
- the impedance of the circuit
- the effective value of current in the circuit.
