Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For the travelling harmonic wave
y (x, t) = 2.0 cos 2π (10t – 0.0080x + 0.35)
Where x and y are in cm and t in s. Calculate the phase difference between oscillatory motion of two points separated by a distance of 4 m.
उत्तर १
Equation for a travelling harmonic wave is given as:
y (x, t) = 2.0 cos 2π (10t – 0.0080x + 0.35)
= 2.0 cos (20 π t – 0.016 π x + 0.70 π)
Where,
Propagation constant, k = 0.0160 π
Amplitude, a = 2 cm
Angular frequency, ω= 20 π rad/s
Phase difference is given by the relation:
`phi = "k"x = (2pi)/lambda`
For x = 4 m = 400 cm
Φ = 0.016 π × 400
= 6.4 π rad
उत्तर २
The given equation can be drawn be rewritten as under
`"y"(x, "t") = 2.0 cos [2pi (10"t" - 0.0080 x) + 2pi xx 0.35]`
or `"y"(x, "t") = 2.0 cos [2pi xx 0.0080((10"t")/0.0080 - x) + 0.7 pi]`
Comparing this equation with the standard equation of a travelling harmonic wave.
`(2pi)/lambda = 2pi xx 0.0080` or `lambda = 1/0.0080 " cm" = 125` cm
The phase difference between oscillatory motion of two points seperated by a distance `trianglex` is given by
`trianglephi = (2pi)/lambda trianglex`
When `triangle z = 4 m = 400` cm then
`trianglephi = (2pi)/125 xx 400`
`= 6.4 pi " rad"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A hospital uses an ultrasonic scanner to locate tumours in a tissue. What is the wavelength of sound in the tissue in which the speed of sound is 1.7 km s–1? The operating frequency of the scanner is 4.2 MHz.
(i) For the wave on a string described in Exercise 15.11, do all the points on the string oscillate with the same (a) frequency, (b) phase, (c) amplitude? Explain your answers. (ii) What is the amplitude of a point 0.375 m away from one end?
A sonometer wire of length l vibrates in fundamental mode when excited by a tuning fork of frequency 416. Hz. If the length is doubled keeping other things same, the string will ______.
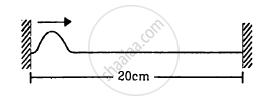
A string of length 20 cm and linear mass density 0⋅40 g cm−1 is fixed at both ends and is kept under a tension of 16 N. A wave pulse is produced at t = 0 near an ends as shown in the figure, which travels towards the other end. (a) When will the string have the shape shown in the figure again? (b) Sketch the shape of the string at a time half of that found in part (a).
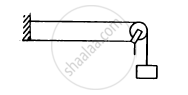
Following figure shows a string stretched by a block going over a pulley. The string vibrates in its tenth harmonic in unison with a particular tuning for. When a beaker containing water is brought under the block so that the block is completely dipped into the beaker, the string vibrates in its eleventh harmonic. Find the density of the material of the block.
A 2⋅00 m-long rope, having a mass of 80 g, is fixed at one end and is tied to a light string at the other end. The tension in the string is 256 N. (a) Find the frequencies of the fundamental and the first two overtones. (b) Find the wavelength in the fundamental and the first two overtones.
A man standing unsymmetrical position between two mountains and fires a gun. He hears the first echo after 1.5 s and the second echo after 2.5 s. If the speed of sound in air is 340 m/s, then the distance between the mountains will be ______
Speed of sound wave in air ______.
A sound wave is passing through air column in the form of compression and rarefaction. In consecutive compressions and rarefactions ______.
If c is r.m.s. speed of molecules in a gas and v is the speed of sound waves in the gas, show that c/v is constant and independent of temperature for all diatomic gases.
