Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
How does drift velocity of electrons in a metallic conductor vary with increase in temperature? Explain.
उत्तर
Drift velocity of electrons in a metallic conductor decreases with increase in temperature.
As we know,
As, we increase the temperature of the metallic conductor the collision between the electrons and ions increases, which results in the decrease in the relaxation time. so, from the equation (4)
vd ∝ r
Hence, the drift velocity decreased.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive an expression for drift velocity of free electrons.
Write its (‘mobility’ of charge carriers) S.I. unit
Estimate the average drift speed of conduction electrons in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 1.0 × 10−7 m2 carrying a current of 1.5 A. Assume the density of conduction electrons to be 9 × 1028 m−3
When electrons drift in a metal from lower to higher potential, does it mean that all the free electrons of the metal are moving in the same direction?
Electrons are emitted by a hot filament and are accelerated by an electric field, as shown in the figure. The two stops at the left ensure that the electron beam has a uniform cross-section.
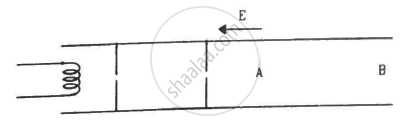
When a current I is set up in a wire of radius r, the drift velocity is vd· If the same current is set up through a wire of radius 2 r, the drift velocity will be:
Metals are good conductor of heat than insulator because
The drift velocity of a free electron inside a conductor is ______
- Consider circuit in figure. How much energy is absorbed by electrons from the initial state of no current (ignore thermal motion) to the state of drift velocity?
- Electrons give up energy at the rate of RI2 per second to the thermal energy. What time scale would one associate with energy in problem (a)? n = no of electron/volume = 1029/m3, length of circuit = 10 cm, cross-section = A = (1mm)2
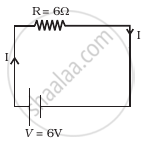
The potential difference applied across a given conductor is doubled. How will this affect (i) the mobility of electrons and (ii) the current density in the conductor? Justify your answers.
