Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
- Consider circuit in figure. How much energy is absorbed by electrons from the initial state of no current (ignore thermal motion) to the state of drift velocity?
- Electrons give up energy at the rate of RI2 per second to the thermal energy. What time scale would one associate with energy in problem (a)? n = no of electron/volume = 1029/m3, length of circuit = 10 cm, cross-section = A = (1mm)2
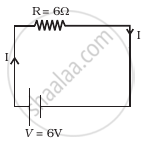
उत्तर
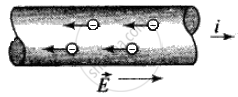
a. Relation between current and drift velocity is given by I = ne Avd, where vd is the drift speed of electrons and n is the number density of electrons.
According to the Ohm's law current in the circuit
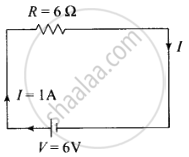
I = V/R
I = 6 V/6 Ω = 1 A
But, I = ne Avd
or vd = `I/("ne A")`
On substituting the values,
For, n = number of electrons/volume = 1029/m3
Length of circuit = 10 cm, cross-section = A = (1 mm)2
`v_d = 1/(10^29 xx 16 xx 10^-19 xx 10^-6)`
= `1/1.6 xx 10^-4` m/s
Therefore, the energy absorbed in the form of KE is given by
Total KE = KE of 1 electron × no. of electrons
KE = `1/2 m_e v_d^2 xx n Al`
= `1/2 xx 9.1 xx 10^31 xx 1/2.56 xx 10^-8 xx 10^29 xx 10^-6 xx 10^-1`
= `2 xx 10^-17 J`
b. Ohmic loss (power loss) is `P = I^2R = 6 xx 1^2 = 6 W = 6 J/s`
Since, the energy dissipated per unit time is the power dissipated.
So, `P = E/t`
Therefore, `E = P xx t`
or `t = E/P = (2 xx 10^17)/6 = 10^17 s`
Important point: The energy dissipated per unit time is the power dissipated `P = (ΔW)/(Δt)`
The power across a resistor is P = I2R.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive an expression for drift velocity of free electrons.
Write its (‘mobility’ of charge carriers) S.I. unit
(a) drift speed
(b) current density
(c) electric current
(d) electric field
Explain the term ‘drift velocity’ of electrons in conductor. Hence obtain the expression for the current through a conductor in terms of ‘drift velocity’.
Consider the following statements.
(A) Free-electron density is different in different metals.
(B) Free-electron density in a metal depends on temperature.
Seebeck Effect is caused _____________ .
Consider the following statements.
(A) Free-electron density is different in different metals.
(B) Free-electron density in a metal depends on temperature.
Peltier Effect is caused _______________ .
Amount of charge in coulomb required to deposit one gram equivalent of substance by electrolysis is:-
The identical conductors maintained at same temperature are given potential difference in the ratio 1 : 2. Then the ratio of their drift velocities is ______.
The relaxation time τ is nearly independent of applied E field whereas it changes significantly with temperature T. First fact is (in part) responsible for Ohm’s law whereas the second fact leads to variation of ρ with temperature. Elaborate why?
Define relaxation time.
