Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is zero,
(a) the electric field must be zero everywhere on the surface
(b) the electric field may be zero everywhere on the surface
(c) the charge inside the surface must be zero
(d) the charge in the vicinity of the surface must be zero
उत्तर
(b) the electric field may be zero everywhere on the surface
(c) the charge inside the surface must be zero
As the flux is zero through the surface, the charge enclosed must be zero. But the electric field is not necessarily zero everywhere on the surface. For example, in the case of a dipole enclosed by the surface, the electric field through the surface is not zero but has some value. So, the correct answers are (b) and (c).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find out the outward flux to a point charge +q placed at the centre of a cube of side ‘a’. Why is it found to be independent of the size and shape of the surface enclosing it? Explain.
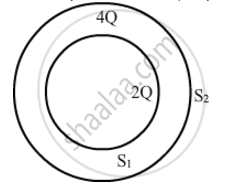
Consider two hollow concentric spheres, S1 and S2, enclosing charges 2Q and 4Q respectively as shown in the figure. (i) Find out the ratio of the electric flux through them. (ii) How will the electric flux through the sphere S1 change if a medium of dielectric constant 'εr' is introduced in the space inside S1 in place of air ? Deduce the necessary expression
Careful measurement of the electric field at the surface of a black box indicates that the net outward flux through the surface of the box is 8.0 × 103 N m2/C.
- What is the net charge inside the box?
- If the net outward flux through the surface of the box were zero, could you conclude that there were no charges inside the box? Why or Why not?
Two charges of magnitudes −2Q and +Q are located at points (a, 0) and (4a, 0) respectively. What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius ‘3a’ with its centre at the origin?
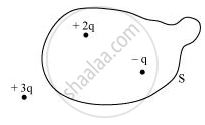
Figure shows three point charges +2q, −q and + 3q. Two charges + 2q and −q are enclosed within a surface ‘S’. What is the electric flux due to this configuration through the surface ‘S’?
A circular ring of radius r made of a non-conducting material is placed with its axis parallel to a uniform electric field. The ring is rotated about a diameter through 180°. Does the flux of the electric field change? If yes, does it decrease or increase?
A charge q is placed at the centre of the open end of a cylindrical vessel (see the figure). The flux of the electric field through the surface of the vessel is ____________ .

Mark the correct options:
The following figure shows a closed surface that intersects a conducting sphere. If a positive charge is placed at point P, the flux of the electric field through the closed surface

Choose the correct answer from given options
The electric flux through a closed Gaussian surface depends upon
If the flux associated with a coil changes at the rate of 360 webers every 4 minutes, then the induced e.m.f. is ______
A uniform electric field of intensity 400 N/C, exists in a certain region. How much flux will cross a given area of 10 cm2 in this region, if the area vector is inclined at 60° to the direction of the field?
A cylinder of radius R and length L is placed in a uniform electric field E parallel to the cylinder axis. The total flux for the surface of the cylinder is given by ______.
The electric field in a region is given by `bar"E" = 4hat"i" + 10hat"j"` N/C. The flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the XZ plane.
In a region of space having a uniform electric field E, a hemispherical bowl of radius r is placed. The electric flux Φ through the bowl is:
A charge Qµc is placed at the centre of a cube the flux coming from any surface will be.
A hollow sphere of radius R has a point charge q at its centre. Electric flux emanating from the sphere is X. How will the electric flux change, if at all, when radius of the sphere is doubled?
