Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Mark the correct options:
पर्याय
Gauss's Law is valid only for symmetrical charge distributions.
Gauss's Law is valid only for charges placed in vacuum.
The electric field calculated by Gauss's Law is the field due to the charge inside the Gaussian surface.
The flux of the electric field through a closed surface due to all the charges is equal to the flux due to the charges enclosed by the surface.
उत्तर
The flux of the electric field through a closed surface due to all the charges is equal to the flux due to the charges enclosed by the surface.
The contribution of flux on the closed surface due to the charges lying outside the surface is zero because number of field line entering the closed surface is equal to the number of field lines coming out of the surface so the net contribution of the charge lying outside the closed surface to the flux is zero. Therefore, the net flux through the surface due to the charge lying outside the the closed surface is zero. The contribution that counts is only due to the charges lying within the closed surface.
Thus, the flux of the electric field through a closed surface due to all the charges (inside and outside the surface) is equal to the flux due to the charges enclosed by the surface
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define electric flux.
Write its (electric flux.) S.I unit.
"The outward electric flux due to charge +Q is independent of the shape and size of the surface which encloses is." Give two reasons to justify this statement.
Consider a uniform electric field E = 3 × 103 `bbhat i` N/C.
- What is the flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the yz plane?
- What is the flux through the same square if the normal to its plane makes a 60° angle with the x-axis?
Careful measurement of the electric field at the surface of a black box indicates that the net outward flux through the surface of the box is 8.0 × 103 N m2/C.
- What is the net charge inside the box?
- If the net outward flux through the surface of the box were zero, could you conclude that there were no charges inside the box? Why or Why not?
A uniformly charged conducting sphere of 2.4 m diameter has a surface charge density of 80.0 μC/m2.
- Find the charge on the sphere.
- What is the total electric flux leaving the surface of the sphere?
Define Electric Flux. Write its SI unit.
Two charges of magnitudes −3Q and + 2Q are located at points (a, 0) and (4a, 0) respectively. What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius ‘5a’ with its centre at the origin?
A small plane area is rotated in an electric field. In which orientation of the area, is the flux of the electric field through the area maximum? In which orientation is it zero?
It is said that any charge given to a conductor comes to its surface. Should all the protons come to the surface? Should all the electrons come to the surface? Should all the free electrons come to the surface?
Electric charges are distributed in a small volume. The flux of the electric field through a spherical surface of radius 10 cm surrounding the total charge is 25 V m. The flux over a concentric sphere of radius 20 cm will be _____________ .
If the flux associated with a coil changes at the rate of 360 webers every 4 minutes, then the induced e.m.f. is ______
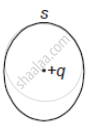
The electric flux through the surface ______.
 |
 |
 |
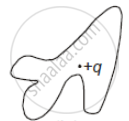 |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) |
A charged particle q is placed at the centre O of cube of length L (A B C D E F G H). Another same charge q is placed at a distance L from O. Then the electric flux through ABCD is ______.
The electric field intensity due to an infinite cylinder of radius R and having charge q per unit length at a distance rir r(r > R) from its axis is ______.
The electric charges are distributed in a small volume. The flux of the electric field through a spherical surface of radius 10 cm surrounding the total charge is 20 V-m. The flux over a concentric sphere of radius 20 cm will be ______.
A hollow sphere of radius R has a point charge Q at its centre. Electric flux emanating from it is `phi`. If both the charge and the radius of the sphere are doubled, electric flux emanating from the sphere will ______.
