Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Mark the correct options:
विकल्प
Gauss's Law is valid only for symmetrical charge distributions.
Gauss's Law is valid only for charges placed in vacuum.
The electric field calculated by Gauss's Law is the field due to the charge inside the Gaussian surface.
The flux of the electric field through a closed surface due to all the charges is equal to the flux due to the charges enclosed by the surface.
उत्तर
The flux of the electric field through a closed surface due to all the charges is equal to the flux due to the charges enclosed by the surface.
The contribution of flux on the closed surface due to the charges lying outside the surface is zero because number of field line entering the closed surface is equal to the number of field lines coming out of the surface so the net contribution of the charge lying outside the closed surface to the flux is zero. Therefore, the net flux through the surface due to the charge lying outside the the closed surface is zero. The contribution that counts is only due to the charges lying within the closed surface.
Thus, the flux of the electric field through a closed surface due to all the charges (inside and outside the surface) is equal to the flux due to the charges enclosed by the surface
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define electric flux.
"The outward electric flux due to charge +Q is independent of the shape and size of the surface which encloses is." Give two reasons to justify this statement.
What is the net flux of the uniform electric field of previous question through a cube of side 20 cm oriented so that its faces are parallel to the coordinate planes?
A uniformly charged conducting sphere of 2.4 m diameter has a surface charge density of 80.0 μC/m2.
- Find the charge on the sphere.
- What is the total electric flux leaving the surface of the sphere?
Two charges of magnitudes −2Q and +Q are located at points (a, 0) and (4a, 0) respectively. What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius ‘3a’ with its centre at the origin?
A thin straight infinitely long conducting wire having charge density λ is enclosed by a cylindrical surface of radius r and length l, its axis coinciding with the length of the wire. Find the expression for the electric flux through the surface of the cylinder.
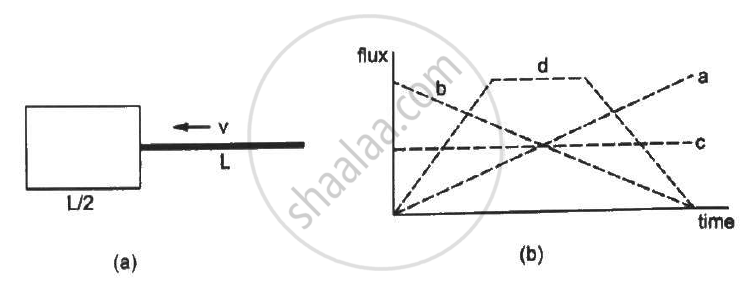
Following Figure (a) shows an imaginary cube of edge L/2. A uniformly charged rod of length (L) moves towards the left at a small but constant speed `nu.` At t = 0, the left end just touches the centre of the face of the cube opposite it. Which of the graphs shown in the figure (b) represents the flux of the electric field through the cube as the rod goes through it?
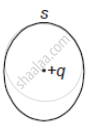
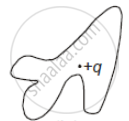
The following figure shows a closed surface that intersects a conducting sphere. If a positive charge is placed at point P, the flux of the electric field through the closed surface

The electric field in a region is given by `vec"E"` = 5 `hatk`N/C. Calculate the electric flux Through a square of side 10.0 cm in the following cases
- The square is along the XY plane
- The square is along XZ plane
- The normal to the square makes an angle of 45° with the Z axis.
If the flux associated with a coil changes at the rate of 360 webers every 4 minutes, then the induced e.m.f. is ______
A uniform electric field of intensity 400 N/C, exists in a certain region. How much flux will cross a given area of 10 cm2 in this region, if the area vector is inclined at 60° to the direction of the field?
The electric flux through the surface ______.
 |
 |
 |
 |
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) |
A charged particle q is placed at the centre O of cube of length L (A B C D E F G H). Another same charge q is placed at a distance L from O. Then the electric flux through ABCD is ______.
A charge Qµc is placed at the centre of a cube the flux coming from any surface will be.
The S.I. unit of electric flux is ______
A circular disc of radius 'r' is placed along the plane of paper. A uniform electric field `vec"E"` is also present in the plane of paper. What amount of electric flux is associated with it?
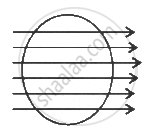
A hollow sphere of radius R has a point charge q at its centre. Electric flux emanating from the sphere is X. How will the electric flux change, if at all, when radius of the sphere is doubled?
A hollow sphere of radius R has a point charge q at its centre. Electric flux emanating from the sphere is X. How will the electric flux change, if at all, when charge q is replaced by an electric dipole?
