Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A charge q is placed at the centre of the open end of a cylindrical vessel (see the figure). The flux of the electric field through the surface of the vessel is ____________ .

विकल्प
zero
q/εv
q/2εv
2q/εv
उत्तर
q/2ε0
According to Gauss's Law, the flux through a closed cylindrical Gaussian surface is q/ε0. But the question is about an open cylindrical vessel. Now, take another identical vessel and make a closed Gaussian surface enclosing the charge, as shown in the following figure.
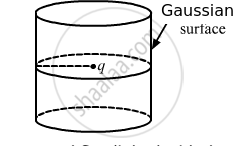
Total flux linked with the closed Gaussian surface,
Ø T =`q/ε_0`
Flux linked with the surface of a open ended cylindrical vessel,
Ø = `(Ø"T")/2 = q/(2ε_0)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define electric flux.
Given a uniform electric field `vecE=5xx10^3hati`N/C, find the flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the y-z plane. What would be the flux through the same square if the plane makes a 30° angle with the x-axis ?
Careful measurement of the electric field at the surface of a black box indicates that the net outward flux through the surface of the box is 8.0 × 103 N m2/C.
- What is the net charge inside the box?
- If the net outward flux through the surface of the box were zero, could you conclude that there were no charges inside the box? Why or Why not?
Two charges of magnitudes +4Q and − Q are located at points (a, 0) and (− 3a, 0) respectively. What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius ‘2a’ with its centre at the origin?
It is said that any charge given to a conductor comes to its surface. Should all the protons come to the surface? Should all the electrons come to the surface? Should all the free electrons come to the surface?
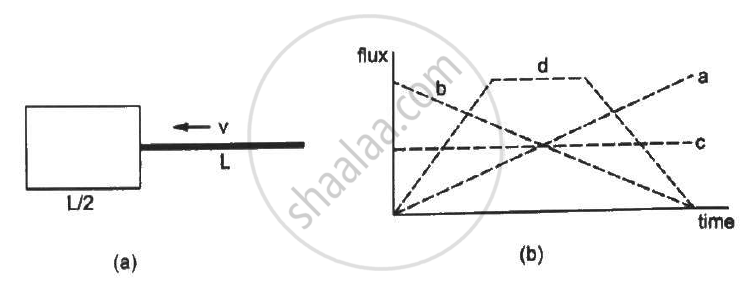
Following Figure (a) shows an imaginary cube of edge L/2. A uniformly charged rod of length (L) moves towards the left at a small but constant speed `nu.` At t = 0, the left end just touches the centre of the face of the cube opposite it. Which of the graphs shown in the figure (b) represents the flux of the electric field through the cube as the rod goes through it?
If the flux of the electric field through a closed surface is zero,
(a) the electric field must be zero everywhere on the surface
(b) the electric field may be zero everywhere on the surface
(c) the charge inside the surface must be zero
(d) the charge in the vicinity of the surface must be zero
The electric field in a region is given by `vec"E"` = 5 `hatk`N/C. Calculate the electric flux Through a square of side 10.0 cm in the following cases
- The square is along the XY plane
- The square is along XZ plane
- The normal to the square makes an angle of 45° with the Z axis.
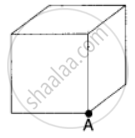
The total flux through the faces of the cube with side of length a if a charge q is placed at corner A of the cube is ______.
A cylinder of radius R and length L is placed in a uniform electric field E parallel to the cylinder axis. The total flux for the surface of the cylinder is given by ______.
The electric field intensity due to an infinite cylinder of radius R and having charge q per unit length at a distance rir r(r > R) from its axis is ______.
A point charge q is placed at a distance a/2 directly above the centre of a square of side a. The electric flux through the square is ______.
The electric field in a region is given by `bar"E" = 4hat"i" + 10hat"j"` N/C. The flux of this field through a square of 10 cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the XZ plane.
In a region of space having a uniform electric field E, a hemispherical bowl of radius r is placed. The electric flux Φ through the bowl is:
What will be the total flux through the faces of the cube (figure) with side of length a if a charge q is placed at

- A: a corner of the cube.
- B: mid-point of an edge of the cube.
- C: centre of a face of the cube.
- D: mid-point of B and C.
A hollow sphere of radius R has a point charge q at its centre. Electric flux emanating from the sphere is X. How will the electric flux change, if at all, when charge q is replaced by an electric dipole?
