Advertisements
Advertisements
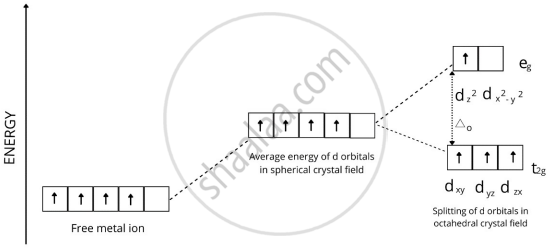
प्रश्न
In a coordination entity, the electronic configuration of the central metal ion is t2g3 eg1
Draw the crystal field splitting diagram for the above complex.
उत्तर
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw figure to show the splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral crystal field.
How are the following conversions carried out?
Benzoic acid into metanitrobenzoic acid.
Draw the structures of the following :
(1) XeF6
(2) IF7
Why are low spin tetrahedral complexes not formed?
Arrange following complex ions in increasing order of crystal field splitting energy (∆O):
\[\ce{[Cr(Cl)6]^{3-}, [Cr(CN)6]^{3-}, [Cr(NH3)6]^{3+}}\].
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment value in the following:
\[\ce{[FeF6]^{3-}, [Fe(H2O)6]^{2+}, [Fe(CN)6]^{4-}}\]
Why are different colours observed in octahedral and tetrahedral complexes for the same metal and same ligands?
The correct order of increasing crystal field strength in following series:
For octahedral Mn(II) and tetrahedral Ni(II) complexes, consider the following statements:
(i) Both the complexes can be high spin.
(ii) Ni(II) complex can very rarely below spin.
(iii) With strong field Ligands, Mn(II) complexes can be low spin.
(iv) Aqueous solution of Mn (II) ions is yellow in colour.
The correct statements are:
Read the passage carefully and answer the questions that follow.
|
Crystal field splitting by various ligands Metal complexes show different colours due to d-d transitions. The complex absorbs light of specific wavelength to promote the electron from t2g to eg level. The colour of the complex is due to the transmitted light, which is complementary of the colour absorbed. The wave number of light absorbed by different complexes of Cr ion are given below:
|
Answer the following questions:
(a) Out of ligands "A", "B", "C" and "D", which ligand causes maximum crystal field splitting? Why?
OR
Which of the two, “A” or “D” will be a weak field ligand? Why?
(b) Which of the complexes will be violet in colour? [CrA6]3- or [CrB6]3+ and why?
(Given: If 560 - 570 nm of light is absorbed, the colour of the complex observed is violet.)
(c) If the ligands attached to Cr3+ ion in the complexes given in the table above are water, cyanide ion, chloride ion, and ammonia (not in this order).
Identify the ligand, write the formula and IUPAC name of the following:
- [CrA6]3-
- [CrC6]3+
