Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a parallelogram ABCD, determine the sum of angles ∠C and ∠D .
उत्तर
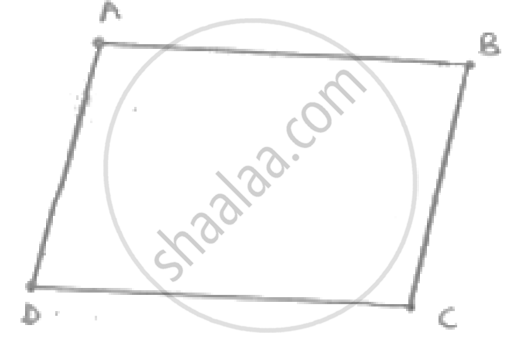
`∠`C and `∠`D are consecutive interior angles on the same side of the transversal CD
∴`∠`C + `∠`D = 180°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a parallelogram ABCD, if `∠`B = 135°, determine the measures of its other angles .
The sides AB and CD of a parallelogram ABCD are bisected at E and F. Prove that EBFD is a parallelogram.
P and Q are the points of trisection of the diagonal BD of a parallelogram AB Prove that CQ is parallel to AP. Prove also that AC bisects PQ.
In a ΔABC median AD is produced to X such that AD = DX. Prove that ABXC is a
parallelogram.
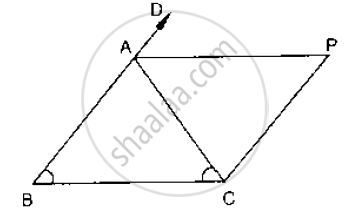
In Fig. below, AB = AC and CP || BA and AP is the bisector of exterior ∠CAD of ΔABC.
Prove that (i) ∠PAC = ∠BCA (ii) ABCP is a parallelogram
In a parallelogram ABCD, if ∠D = 115°, then write the measure of ∠A.
PQRS is a quadrilateral, PR and QS intersect each other at O. In which of the following case, PQRS is a parallelogram?
∠P = 100°, ∠Q = 80°, ∠R = 95°
P is the mid-point of side BC of a parallelogram ABCD such that ∠BAP = ∠DAP. If AD = 10 cm, then CD =
In the given figure, ∠A = 64°, ∠ABC = 58°. If BO and CO are the bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACB respectively of ΔABC, find x° and y°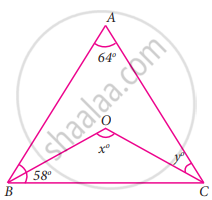
In the given Figure, if AB = 2, BC = 6, AE = 6, BF = 8, CE = 7, and CF = 7, compute the ratio of the area of quadrilateral ABDE to the area of ΔCDF. (Use congruent property of triangles)
