Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In parallelogram MODE, the bisector of ∠M and ∠O meet at Q, find the measure of ∠MQO.
उत्तर
Let MODE be a parallelogram and Q be the point of intersection of the bisector of ∠M and ∠O.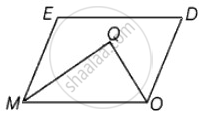
Since, MODE is a parallelogram
∴ ∠EMO + ∠DOM = 180° ...[∵ Adjacent angles are supplementary]
⇒ `1/2` ∠EMO + `1/2` ∠DOM = 90° ...[Dividing both sides by 2]
⇒ ∠QMO + ∠QOM = 90° ...(i)
Now, In ΔMOQ,
∠QOM + ∠QMO + ∠MQO = 180° ...[Angle sum property of triangle]
⇒ 90° + ∠MQO = 180° ...[From equation (i)]
∴ ∠MQO = 180° – 90° = 90°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Given a parallelogram ABCD. Complete each statement along with the definition or property used.
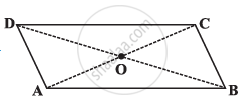
- AD = ______
- ∠DCB = ______
- OC = ______
- m∠DAB + m∠CDA = ______
Consider the given parallelogram. Find the values of the unknowns x, y, z.

Can a quadrilateral ABCD be a parallelogram if AB = DC = 8 cm, AD = 4 cm and BC = 4.4 cm?
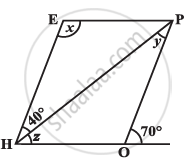
The adjacent figure HOPE is a parallelogram. Find the angle measures x, y and z. State the properties you use to find them.
In parallelogram PQRS, ∠Q = (4x – 5)° and ∠S = (3x + 10)°. Calculate: ∠Q and ∠R.
ABCD is a parallelogram. What kind of quadrilateral is it if: AC = BD but AC is not perpendicular to BD?
If a triangle and a parallelogram lie on the same base and between the same parallels, then prove that the area of the triangle is equal to half of the area of parallelogram
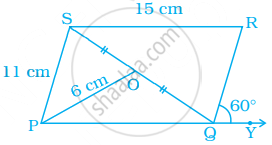
In parallelogram PQRS, O is the mid point of SQ. Find ∠S, ∠R, PQ, QR and diagonal PR.
ABCD is a parallelogram. Find the value of x, y and z.

ABCD is a parallelogram. The bisector of angle A intersects CD at X and bisector of angle C intersects AB at Y. Is AXCY a parallelogram? Give reason.
