Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In parallelogram MODE, the bisector of ∠M and ∠O meet at Q, find the measure of ∠MQO.
Solution
Let MODE be a parallelogram and Q be the point of intersection of the bisector of ∠M and ∠O.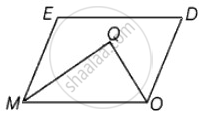
Since, MODE is a parallelogram
∴ ∠EMO + ∠DOM = 180° ...[∵ Adjacent angles are supplementary]
⇒ `1/2` ∠EMO + `1/2` ∠DOM = 90° ...[Dividing both sides by 2]
⇒ ∠QMO + ∠QOM = 90° ...(i)
Now, In ΔMOQ,
∠QOM + ∠QMO + ∠MQO = 180° ...[Angle sum property of triangle]
⇒ 90° + ∠MQO = 180° ...[From equation (i)]
∴ ∠MQO = 180° – 90° = 90°
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The measures of two adjacent angles of a parallelogram are in the ratio 3 : 2. Find the measure of each of the angles of the parallelogram.
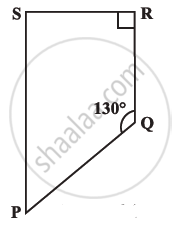
Find the measure of ∠P and ∠S, if `bar(SP) || bar(RQ)` in the following figure. (If you find m∠R, is there more than one method to find m∠P?).
Perimeter of a parallelogram is 150 cm. One of its sides is greater than the other side by 25 cm. Find the lengths of all sides.
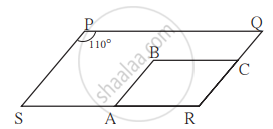
In the given figure, `square`PQRS and `square`ABCR are two parallelograms. If ∠P = 110° then find the measures of all angles of `square`ABCR.
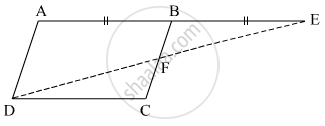
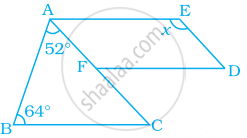
In the given figure, `square`ABCD is a parallelogram. Point E is on the ray AB such that BE = AB then prove that line ED bisects seg BC at point F.
Construct a parallelogram ABCD such that l(BC) = 7 cm, m∠ABC = 40° , l(AB) = 3 cm.
A diagonal of a parallelogram bisects an angle. Will it also bisect the other angle? Give reason.
In the following figure, FD || BC || AE and AC || ED. Find the value of x.
Construct a parallelogram when one of its side is 4 cm and its two diagonals are 5.6 cm and 7 cm. Measure the other side.
Draw a rough figure of a quadrilateral that is not a parallelogram but has exactly two opposite angles of equal measure.
