Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
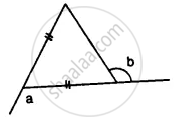
In the given figure, express a in terms of b.
उत्तर
In Δ ABC,
BC = BA
∴ ∠BCA = ∠BAC
and Ext. ∠CBE = ∠BCA + ∠BAC
⇒ a = ∠BCA + ∠BCA
⇒ a = 2 ∠BCA .........(i)
But ∠ACB = 180° − b ..........(∵ ∠ACD and ∠ACB are linear pair)
⇒ ∠BCA = 180° − b .............(ii)
∴ a = 2 ∠BCA = 2 (180° − b)
= 360°− 2b
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two angles of a triangle are equal and the third angle is greater than each of those angles
by 30°. Determine all the angles of the triangle.
ABC is a triangle in which ∠A — 72°, the internal bisectors of angles B and C meet in O.
Find the magnitude of ∠BOC.
Is the following statement true and false :
All the angles of a triangle can be greater than 60°.
In Δ ABC, BD⊥ AC and CE ⊥ AB. If BD and CE intersect at O, prove that ∠BOC = 180° − A.
Side BC of a triangle ABC has been produced to a point D such that ∠ACD = 120°. If ∠B = \[\frac{1}{2}\]∠A is equal to
An exterior angle of a triangle is 108° and its interior opposite angles are in the ratio 4 : 5. The angles of the triangle are
Classify the following triangle according to sides:
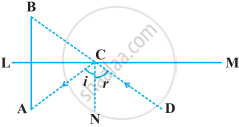
The image of an object placed at a point A before a plane mirror LM is seen at the point B by an observer at D as shown in the following figure. Prove that the image is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror.
[Hint: CN is normal to the mirror. Also, angle of incidence = angle of reflection].
Can we have two acute angles whose sum is an obtuse angle? Why or why not?
Which two triangles have ∠B in common?