Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
It is required to reduce the volume of a gas by 20% by compressing it at a constant pressure. To do so, the gas has to be cooled. If the gas attains a final temperature of 157°C, find the initial temperature of the gas.
उत्तर
Initial conditions:
V1 = Initial volume of the gas = V
T1 = Initial temperature of the gas = ?
Final conditions:
V2 (Final volume) = reduce by 20%
= V - `20/100` of V
= `(80"V")/100`
= `(4"V")/5`
T2 = Final temperature of the gas = 157°C = 157 + 273 = 430 K
By Charles Law:
`"V"_1/"T"_1 = "V"_2/"T"_2`
Substituting the values:
`"V"/"T"_1 = ((4"V")/5)/430`
`1/"T"_1 = 4/(5 xx 430)`
T1 = `(430 xx 5)/4`
T1 = 537.5 K
Therefore, final temperature of the gas = 537.5 K - 273 K = 264.5°C
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the law which is represented by the following graph:
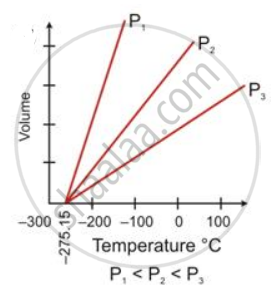
How did Charles's law lead to the concept of an absolute scale of temperature?
State the following:
Ice point in absolute temperature
88 cm3 of nitrogen is at a pressure of 770 mm mercury. If the pressure is raised to 880 mmHg, find by how much the volume will diminish, the temperature remaining constant.
Taking the volume of hydrogen as calculated in Q.19, what change must be made in Kelvin (absolute) temperature to return the volume to 2500 cm3 (pressure remaining constant)?
State Charles's law.
Fill in the blank with the correct word, from the words in option:
At -273°C the volume of a gas is theoretically ______.
A fixed volume of a gas occupies 760cm3 at 27°C and 70 cm of Hg. What will be its vol. at s.t.p.
The pressure on one mole of gas at s.t.p. is doubled and the temperature is raised to 546 K. What is the final volume of the gas ? [one mole of a gas occupies a volume of 22.4 litres at stp.]
According to Charles’s law, at constant pressure, the temperature is inversely proportional to volume.
