Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Let Q and W denote the amount of heat given to an ideal gas and the work done by it in an isothermal process.
पर्याय
Q = 0
W = 0
Q ≠ W
Q = W
उत्तर
Q = W
In an isothermal process, temperature of the system stays constant, i.e. there's no change in internal energy. Thus, U = 0, where U denotes the change in internal energy of the system. According to the first law of thermodynamics, heat supplied to the system is equal to the sum of change in internal energy and work done by the system, such that Q = U + W. As U = 0, Q = W.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The energy of a given sample of an ideal gas depends only on its
Keeping the number of moles, volume and temperature the same, which of the following are the same for all ideal gases?
The average momentum of a molecule in a sample of an ideal gas depends on
Consider the quantity \[\frac{MkT}{pV}\] of an ideal gas where M is the mass of the gas. It depends on the
Calculate the volume of 1 mole of an ideal gas at STP.
Let Q and W denote the amount of heat given to an ideal gas and the work done by it in an adiabatic process.
(a) Q = 0
(b) W = 0
(c) Q = W
(d) Q ≠ W
A vessel containing one mole of a monatomic ideal gas (molecular weight = 20 g mol−1) is moving on a floor at a speed of 50 m s−1. The vessel is stopped suddenly. Assuming that the mechanical energy lost has gone into the internal energy of the gas, find the rise in its temperature.
An amount Q of heat is added to a monatomic ideal gas in a process in which the gas performs a work Q/2 on its surrounding. Find the molar heat capacity for the process
Two ideal gases have the same value of Cp / Cv = γ. What will be the value of this ratio for a mixture of the two gases in the ratio 1 : 2?
The volume of an ideal gas (γ = 1.5) is changed adiabatically from 4.00 litres to 3.00 litres. Find the ratio of (a) the final pressure to the initial pressure and (b) the final temperature to the initial temperature.
An ideal gas at pressure 2.5 × 105 Pa and temperature 300 K occupies 100 cc. It is adiabatically compressed to half its original volume. Calculate (a) the final pressure (b) the final temperature and (c) the work done by the gas in the process. Take γ = 1.5
Two vessels A and B of equal volume V0 are connected by a narrow tube that can be closed by a valve. The vessels are fitted with pistons that can be moved to change the volumes. Initially, the valve is open and the vessels contain an ideal gas (Cp/Cv = γ) at atmospheric pressure p0 and atmospheric temperature T0. The walls of vessel A are diathermic and those of B are adiabatic. The valve is now closed and the pistons are slowly pulled out to increase the volumes of the vessels to double the original value. (a) Find the temperatures and pressures in the two vessels. (b) The valve is now opened for sufficient time so that the gases acquire a common temperature and pressure. Find the new values of the temperature and pressure.
An ideal gas of density 1.7 × 10−3 g cm−3 at a pressure of 1.5 × 105 Pa is filled in a Kundt's tube. When the gas is resonated at a frequency of 3.0 kHz, nodes are formed at a separation of 6.0 cm. Calculate the molar heat capacities Cp and Cv of the gas.
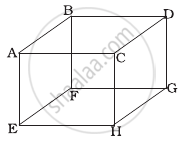
1 mole of an ideal gas is contained in a cubical volume V, ABCDEFGH at 300 K (Figure). One face of the cube (EFGH) is made up of a material which totally absorbs any gas molecule incident on it. At any given time ______.
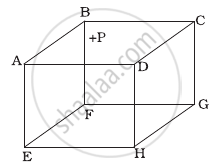
ABCDEFGH is a hollow cube made of an insulator (Figure). Face ABCD has positive charge on it. Inside the cube, we have ionized hydrogen. The usual kinetic theory expression for pressure ______.
- will be valid.
- will not be valid since the ions would experience forces other than due to collisions with the walls.
- will not be valid since collisions with walls would not be elastic.
- will not be valid because isotropy is lost.
When an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically, its temperature rises: the molecules on the average have more kinetic energy than before. The kinetic energy increases ______.
- because of collisions with moving parts of the wall only.
- because of collisions with the entire wall.
- because the molecules gets accelerated in their motion inside the volume.
- because of redistribution of energy amongst the molecules.
The container shown in figure has two chambers, separated by a partition, of volumes V1 = 2.0 litre and V2 = 3.0 litre. The chambers contain µ1 = 4.0 and µ2 = 5.0 moles of a gas at pressures p1 = 1.00 atm and p2 = 2.00 atm. Calculate the pressure after the partition is removed and the mixture attains equilibrium.
| V1 | V2 |
| µ1, p1 | µ2 |
| p2 |
