Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Maximize Z = 7x + 10y
Subject to
\[x + y \leq 30000\]
\[ y \leq 12000\]
\[ x \geq 6000\]
\[ x \geq y\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
उत्तर
We have to maximize Z = 7x + 10y
First, we will convert the given inequations into equations, we obtain the following equations:
x + y = 30000,y = 12000, x = 6000, x = y, x = 0 and y = 0.
Region represented by x + y ≤ 30000:
The line x + y = 30000 meets the coordinate axes at \[A\left( 30000, 0 \right)\] and \[B\left( 0, 30000 \right)\] respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line x + y = 30000.
Clearly (0,0) satisfies the inequation x + y ≤ 30000. So,the region containing the origin represents the solution set of the inequation x + y ≤ 30000.
The line y = 12000 is the line that passes through C(0,12000) and parallel to x axis.
The line x = 6000 is the line that passes through (6000, 0) and parallel to y axis.
Region represented by x ≥ y
The line x = y is the line that passes through origin.The points to the right of the line x= y satisfy the inequation x ≥ y.
Like by taking the point (−12000, 6000).Here, 6000 > −12000 which implies y > x. Hence, the points to the left of the line x = y will not satisfy the given inequation x ≥ y.
Region represented by x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0:
Since, every point in the first quadrant satisfies these inequations. So, the first quadrant is the region represented by the inequations x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0.
The feasible region determined by the system of constraints, x + y ≤ 30000, y ≤ 12000, x ≥ 6000, x ≥ y , x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0 are as follows:
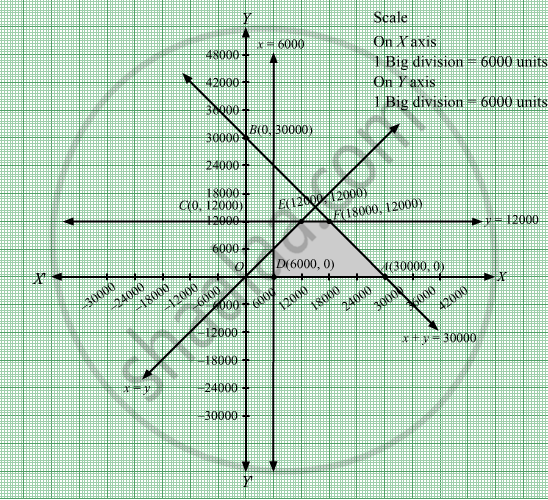
The corner points of the feasible region are D(6000, 0), \[A\left( 3000, 0 \right)\] , \[F\left( 18000, 12000 \right)\] and \[E\left( 12000, 12000 \right)\] .
The values of Z at these corner points are as follows:
| Corner point | Z = 7x + 10y |
| D(6000, 0) | 7 × 6000 + 10 × 0 = 42000 |
|
\[A\left( 3000, 0 \right)\]
|
7× 3000 + 10 × 0 = 21000 |
|
\[F\left( 18000, 12000 \right)\]
|
7 × 18000 + 10 × 12000 = 246000 |
|
\[E\left( 12000, 12000 \right)\]
|
7 × 12000 + 10 ×12000 = 204000 |
We see that the maximum value of the objective function Z is 246000 which is at \[F\left( 18000, 12000 \right)\] that means at x = 18000 and y = 12000.
Thus, the optimal value of Z is 246000.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A dealer in rural area wishes to purchase a number of sewing machines. He has only Rs 5,760 to invest and has space for at most 20 items for storage. An electronic sewing machine cost him Rs 360 and a manually operated sewing machine Rs 240. He can sell an electronic sewing machine at a profit of Rs 22 and a manually operated sewing machine at a profit of Rs 18. Assuming that he can sell all the items that he can buy, how should he invest his money in order to maximize his profit? Make it as a LPP and solve it graphically.
Solve the following L.P.P graphically:
Maximize: Z = 10x + 25y
Subject to: x ≤ 3, y ≤ 3, x + y ≤ 5, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
A retired person wants to invest an amount of Rs. 50, 000. His broker recommends investing in two type of bonds ‘A’ and ‘B’ yielding 10% and 9% return respectively on the invested amount. He decides to invest at least Rs. 20,000 in bond ‘A’ and at least Rs. 10,000 in bond ‘B’. He also wants to invest at least as much in bond ‘A’ as in bond ‘B’. Solve this linear programming problem graphically to maximise his returns.
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically :
Maximise Z = 7x + 10y subject to the constraints
4x + 6y ≤ 240
6x + 3y ≤ 240
x ≥ 10
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Minimize Z = 18x + 10y
Subject to
\[4x + y \geq 20\]
\[2x + 3y \geq 30\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 15x + 10y
Subject to
\[3x + 2y \leq 80\]
\[2x + 3y \leq 70\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 2x + 3y
Subject to
\[x + y \geq 1\]
\[10x + y \geq 5\]
\[x + 10y \geq 1\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Find the maximum and minimum value of 2x + y subject to the constraints:
x + 3y ≥ 6, x − 3y ≤ 3, 3x + 4y ≤ 24, − 3x + 2y ≤ 6, 5x + y ≥ 5, x, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following LPP graphically:
Maximize Z = 20 x + 10 y
Subject to the following constraints
\[x +\]2\[y \leq\]28
3x+ \[y \leq\]24
\[x \geq\] 2x.
\[y \geq\] 0
One kind of cake requires 300 gm of flour and 15 gm of fat, another kind of cake requires 150 gm of flour and 30 gm of fat. Find the maximum number of cakes which can be made from 7.5 kg of flour and 600 gm of fat, assuming that there is no shortage of the other ingradients used in making the cake. Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
Reshma wishes to mix two types of food P and Q in such a way that the vitamin contents of the mixture contains at least 8 units of vitamin A and 11 units of vitamin B. Food P costs ₹60/kg and food Q costs ₹80/kg. Food P contains 3 units/kg of vitamin A and 5 units/kg of vitamin B while food Q contains 4 units/kg of vitamin A and 2 units/kg of vitamin B. Determine the minimum cost of the mixture.
A dietician has to develop a special diet using two foods P and Q. Each packet (containing 30 g) of food P contains 12 units of calcium, 4 units of iron, 6 units of cholesterol and 6 units of vitamin A. Each packet of the same quantity of food Q contains 3 units of calcium, 20 units of iron, 4 units of cholesterol and 3 units of vitamin A. The diet requires atleast 240 units of calcium, atleast 460 units of iron and at most 300 units of cholesterol. How many packets of each food should be used to minimise the amount of vitamin A in the diet? What is the minimum of vitamin A.
A dietician wishes to mix together two kinds of food X and Y in such a way that the mixture contains at least 10 units of vitamin A, 12 units of vitamin B and 8 units of vitamin C. The vitamin contents of one kg food is given below:
| Food | Vitamin A | Vitamin B | Vitamin C |
| X | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Y | 2 | 2 | 1 |
One kg of food X costs ₹16 and one kg of food Y costs ₹20. Find the least cost of the mixture which will produce the required diet?
Two tailors, A and B earn Rs 15 and Rs 20 per day respectively. A can stitch 6 shirts and 4 pants while B can stitch 10 shirts and 4 pants per day. How many days shall each work if it is desired to produce (at least) 60 shirts and 32 pants at a minimum labour cost?
A small manufacturer has employed 5 skilled men and 10 semi-skilled men and makes an article in two qualities deluxe model and an ordinary model. The making of a deluxe model requires 2 hrs. work by a skilled man and 2 hrs. work by a semi-skilled man. The ordinary model requires 1 hr by a skilled man and 3 hrs. by a semi-skilled man. By union rules no man may work more than 8 hrs per day. The manufacturers clear profit on deluxe model is Rs 15 and on an ordinary model is Rs 10. How many of each type should be made in order to maximize his total daily profit.
A manufacturer produces two types of steel trunks. He has two machines A and B. For completing, the first types of the trunk requires 3 hours on machine A and 3 hours on machine B, whereas the second type of the trunk requires 3 hours on machine A and 2 hours on machine B. Machines A and B can work at most for 18 hours and 15 hours per day respectively. He earns a profit of Rs 30 and Rs 25 per trunk of the first type and the second type respectively. How many trunks of each type must he make each day to make maximum profit?
A manufacturer of patent medicines is preparing a production plan on medicines, A and B. There are sufficient raw materials available to make 20000 bottles of A and 40000 bottles of B, but there are only 45000 bottles into which either of the medicines can be put. Further, it takes 3 hours to prepare enough material to fill 1000 bottles of A, it takes 1 hour to prepare enough material to fill 1000 bottles of B and there are 66 hours available for this operation. The profit is Rs 8 per bottle for A and Rs 7 per bottle for B. How should the manufacturer schedule his production in order to maximize his profit?
A firm manufactures two types of products A and B and sells them at a profit of Rs 5 per unit of type A and Rs 3 per unit of type B. Each product is processed on two machines M1 and M2. One unit of type A requires one minute of processing time on M1 and two minutes of processing time on M2, whereas one unit of type B requires one minute of processing time on M1 and one minute on M2. Machines M1 and M2 are respectively available for at most 5 hours and 6 hours in a day. Find out how many units of each type of product should the firm produce a day in order to maximize the profit. Solve the problem graphically.
If a young man drives his vehicle at 25 km/hr, he has to spend ₹2 per km on petrol. If he drives it at a faster speed of 40 km/hr, the petrol cost increases to ₹5 per km. He has ₹100 to spend on petrol and travel within one hour. Express this as an LPP and solve the same.
A merchant plans to sell two types of personal computers a desktop model and a portable model that will cost Rs 25,000 and Rs 40,000 respectively. He estimates that the total monthly demand of computers will not exceed 250 units. Determine the number of units of each type of computers which the merchant should stock to get maximum profit if he does not want to invest more than Rs 70 lakhs and his profit on the desktop model is Rs 4500 and on the portable model is Rs 5000.
A manufacturer produces two products A and B. Both the products are processed on two different machines. The available capacity of first machine is 12 hours and that of second machine is 9 hours per day. Each unit of product A requires 3 hours on both machines and each unit of product B requires 2 hours on first machine and 1 hour on second machine. Each unit of product A is sold at ₹7 profit and that of B at a profit of ₹4. Find the production level per day for maximum profit graphically.
Tow godowns, A and B, have grain storage capacity of 100 quintals and 50 quintals respectively. They supply to 3 ration shops, D, E and F, whose requirements are 60, 50 and 40 quintals respectively. The cost of transportation per quintal from the godowns to the shops are given in the following table:
| Transportation cost per quintal(in Rs.) | ||
| From-> | A | B |
| To | ||
| D | 6.00 | 4.00 |
| E | 3.00 | 2.00 |
| F | 2.50 | 3.00 |
How should the supplies be transported in order that the transportation cost is minimum?
The value of objective function is maximum under linear constraints ______.
A company manufactures two types of novelty souvenirs made of plywood. Souvenirs of type A
require 5 minutes each for cutting and 10 minutes each for assembling. Souvenirs of type B require 8 minutes each for cutting and 8 minutes each for assembling. There are 3 hours and 20 minutes available for cutting and 4 hours available for assembling. The profit is Rs. 50 each for type A and Rs. 60 each for type B souvenirs. How many souvenirs of each type should the company manufacture in order to maximize profit? Formulate the above LPP and solve it graphically and also find the maximum profit.
A company manufactures two types of cardigans: type A and type B. It costs ₹ 360 to make a type A cardigan and ₹ 120 to make a type B cardigan. The company can make at most 300 cardigans and spend at most ₹ 72000 a day. The number of cardigans of type B cannot exceed the number of cardigans of type A by more than 200. The company makes a profit of ₹ 100 for each cardigan of type A and ₹ 50 for every cardigan of type B.
Formulate this problem as a linear programming problem to maximize the profit to the company. Solve it graphically and find the maximum profit.
The graph of the inequality 3X − 4Y ≤ 12, X ≤ 1, X ≥ 0, Y ≥ 0 lies in fully in
For L.P.P. maximize z = 4x1 + 2x2 subject to 3x1 + 2x2 ≥ 9, x1 - x2 ≤ 3, x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0 has ______.
Area of the region bounded by y = cos x, x = 0, x = π and X-axis is ______ sq.units.
The maximum of z = 5x + 2y, subject to the constraints x + y ≤ 7, x + 2y ≤ 10, x, y ≥ 0 is ______.
A set of values of decision variables which satisfies the linear constraints and nn-negativity conditions of an L.P.P. is called its ____________.
Let R be the feasible region for a linear programming problem, and let Z = ax + by be the objective function. If R is bounded, then the objective function Z has both a maximum and a minimum value on R and ____________.
In Corner point method for solving a linear programming problem the first step is to ____________.
Which of the statements describe the solution set for `-2(x + 8) = - 2x + 20`?
The comer point of the feasible region determined by the following system of linear inequalities:
2x + y ≤ 10, x + 3y ≤ 15, x, y ≥ 0 are (0, 0), (5, 0), (3, 4) and (0, 5). Let x = Px + qx where P, q > 0 condition on P and Q so that the maximum of z occurs at both (3, 4) and (0, 5) is
The constraints –x1 + x2 ≤ 1, –x1 + 3x2 ≤ 9, x1x2 ≥ 0 define on ______.
The maximum value of z = 5x + 2y, subject to the constraints x + y ≤ 7, x + 2y ≤ 10, x, y ≥ 0 is ______.
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically:
Minimize: Z = 5x + 10y
Subject to constraints:
x + 2y ≤ 120, x + y ≥ 60, x – 2y ≥ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Minimize: Z = 60x + 80y
Subject to constraints:
3x + 4y ≥ 8
5x + 2y ≥ 11
x, y ≥ 0
