Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A manufacturer of patent medicines is preparing a production plan on medicines, A and B. There are sufficient raw materials available to make 20000 bottles of A and 40000 bottles of B, but there are only 45000 bottles into which either of the medicines can be put. Further, it takes 3 hours to prepare enough material to fill 1000 bottles of A, it takes 1 hour to prepare enough material to fill 1000 bottles of B and there are 66 hours available for this operation. The profit is Rs 8 per bottle for A and Rs 7 per bottle for B. How should the manufacturer schedule his production in order to maximize his profit?
उत्तर
Let x bottles of medicine A and y bottles of medicine B are prepared.
Number of bottles cannot be negative.
Therefore,
\[x, y \geq 0\] According to question, the constraints are
\[x \leq 20000\]
\[y \leq 40000\]
\[x + y \leq 45000\]
Time taken to fill one bottle of A is \[\frac{3}{1000}\] hrs and time taken by to fill one bottle of B is \[\frac{1}{1000}\] hrs . Therefore, time taken to fill x bottles of A and y bottles of B is \[\frac{3x}{1000}\] hrs and \[\frac{y}{1000}\]hrs respectively.
Total profit = Z = \[8x + 7y\] which is to be maximised.
Max Z = \[8x + 7y\]
\[x \leq 20000\]
\[y \leq 40000\]
\[x + y \leq 45000\]
x =20000, y = 40000, x + y = 45000, 3x + y = 66000, x = 0 and y = 0
Region represented by x ≤ 20000:
The line x = 20000 is the line that passes through A1(20000, 0) and is parallel to Y axis.The region to the left of the line x = 20000 will satisfy the inequation x ≤ 20000.
Region represented by y ≤ 40000:
The line y = 40000 is the line that passes through B1(0, 40000) and is parallel to X axis.The region below the line y = 40000 will satisfy the inequation y ≤ 40000.
Region represented by x + y ≤ 45000:
The line x + y = 45000 meets the coordinate axes at C1(45000, 0) and D1(0, 45000) respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line x + y = 45000. Clearly (0,0) satisfies the inequation x + y ≤ 45000. So,the region which contains the origin represents the solution set of the inequation x + y ≤ 45000.
Region represented by 3x + y ≤ 66000:
The line 3x + y = 66000 meets the coordinate axes at E1(22000, 0) and \[F_1 \left( 0, 66000 \right)\] respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line 3x + y = 66000. Clearly (0,0) satisfies the inequation 3x + y ≤ 66000. So,the region which contains the origin represents the solution set of the inequation 3x + y ≤ 66000.
Region represented by x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0:
Since, every point in the first quadrant satisfies these inequations. So, the first quadrant is the region represented by the inequations x ≥ 0, and y ≥ 0.
The feasible region determined by the system of constraints x ≤ 20000, y ≤ 40000, x + y≤ 45000, 3x + y ≤ 66000, x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0 are as follows.
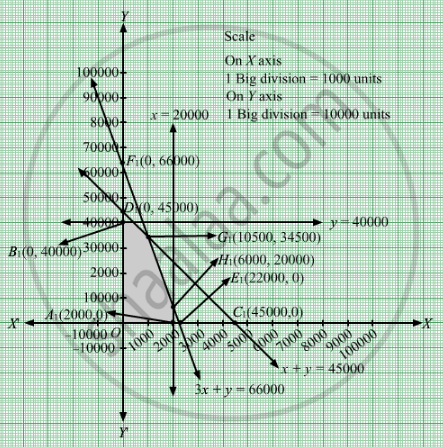 The corner points are O(0, 0), B1(0, 40000), G1(10500, 34500), H1(6000, 20000) and A1(20000, 0).
The corner points are O(0, 0), B1(0, 40000), G1(10500, 34500), H1(6000, 20000) and A1(20000, 0). The values of Z at these corner points are as follows
| Corner point | Z= 8x + 7y |
| O | 0 |
| B1 | 280000 |
| G1 | 325500 |
| H1 | 188000 |
| A1 | 160000 |
The maximum value of Z is 325500 which is attained at G1(10500, 34500).
Thus, the maximum profit is Rs 325500 obtained when 10500 bottles of A and 34500 bottles of B were manufactured.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Minimize : Z = 6x + 4y
Subject to the conditions:
3x + 2y ≥ 12,
x + y ≥ 5,
0 ≤ x ≤ 4,
0 ≤ y ≤ 4
A dealer in rural area wishes to purchase a number of sewing machines. He has only Rs 5,760 to invest and has space for at most 20 items for storage. An electronic sewing machine cost him Rs 360 and a manually operated sewing machine Rs 240. He can sell an electronic sewing machine at a profit of Rs 22 and a manually operated sewing machine at a profit of Rs 18. Assuming that he can sell all the items that he can buy, how should he invest his money in order to maximize his profit? Make it as a LPP and solve it graphically.
Solve the following L.P.P graphically:
Maximize: Z = 10x + 25y
Subject to: x ≤ 3, y ≤ 3, x + y ≤ 5, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Find graphically, the maximum value of z = 2x + 5y, subject to constraints given below :
2x + 4y ≤ 83
x + y ≤ 6
x + y ≤ 4
x ≥ 0, y≥ 0
A company manufactures bicycles and tricycles each of which must be processed through machines A and B. Machine A has maximum of 120 hours available and machine B has maximum of 180 hours available. Manufacturing a bicycle requires 6 hours on machine A and 3 hours on machine B. Manufacturing a tricycle requires 4 hours on machine A and 10 hours on machine B.
If profits are Rs. 180 for a bicycle and Rs. 220 for a tricycle, formulate and solve the L.P.P. to determine the number of bicycles and tricycles that should be manufactured in order to maximize the profit.
Solve the following L.P.P. graphically Maximise Z = 4x + y
Subject to following constraints x + y ≤ 50
3x + y ≤ 90,
x ≥ 10
x, y ≥ 0
Maximise z = 8x + 9y subject to the constraints given below :
2x + 3y ≤ 6
3x − 2y ≤6
y ≤ 1
x, y ≥ 0
Maximize Z = 4x + 3y
Subject to
\[3x + 4y \leq 24\]
\[8x + 6y \leq 48\]
\[ x \leq 5\]
\[ y \leq 6\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically:
Minimize z = 6 x + 3 y
Subject to the constraints:
4 x + \[y \geq\] 80
x + 5 \[y \geq\] 115
3 x + 2 \[y \leq\] 150
\[x \geq\] 0 , \[y \geq\] 0
Reshma wishes to mix two types of food P and Q in such a way that the vitamin contents of the mixture contains at least 8 units of vitamin A and 11 units of vitamin B. Food P costs ₹60/kg and food Q costs ₹80/kg. Food P contains 3 units/kg of vitamin A and 5 units/kg of vitamin B while food Q contains 4 units/kg of vitamin A and 2 units/kg of vitamin B. Determine the minimum cost of the mixture.
A dietician has to develop a special diet using two foods P and Q. Each packet (containing 30 g) of food P contains 12 units of calcium, 4 units of iron, 6 units of cholesterol and 6 units of vitamin A. Each packet of the same quantity of food Q contains 3 units of calcium, 20 units of iron, 4 units of cholesterol and 3 units of vitamin A. The diet requires atleast 240 units of calcium, atleast 460 units of iron and at most 300 units of cholesterol. How many packets of each food should be used to minimise the amount of vitamin A in the diet? What is the minimum of vitamin A.
If a young man drives his vehicle at 25 km/hr, he has to spend Rs 2 per km on petrol. If he drives it at a faster speed of 40 km/hr, the petrol cost increases to Rs 5/per km. He has Rs 100 to spend on petrol and travel within one hour. Express this as an LPP and solve the same.
A company produces two types of leather belts, say type A and B. Belt A is a superior quality and belt B is of a lower quality. Profits on each type of belt are Rs 2 and Rs 1.50 per belt, respectively. Each belt of type A requires twice as much time as required by a belt of type B. If all belts were of type B, the company could produce 1000 belts per day. But the supply of leather is sufficient only for 800 belts per day (both A and B combined). Belt A requires a fancy buckle and only 400 fancy buckles are available for this per day. For belt of type B, only 700 buckles are available per day.
How should the company manufacture the two types of belts in order to have a maximum overall profit?
A manufacturer of Furniture makes two products : chairs and tables. processing of these products is done on two machines A and B. A chair requires 2 hrs on machine A and 6 hrs on machine B. A table requires 4 hrs on machine A and 2 hrs on machine B. There are 16 hrs of time per day available on machine A and 30 hrs on machine B. Profit gained by the manufacturer from a chair and a table is Rs 3 and Rs 5 respectively. Find with the help of graph what should be the daily production of each of the two products so as to maximize his profit.
A firm manufactures two types of products A and B and sells them at a profit of Rs 5 per unit of type A and Rs 3 per unit of type B. Each product is processed on two machines M1 and M2. One unit of type A requires one minute of processing time on M1 and two minutes of processing time on M2, whereas one unit of type B requires one minute of processing time on M1 and one minute on M2. Machines M1 and M2 are respectively available for at most 5 hours and 6 hours in a day. Find out how many units of each type of product should the firm produce a day in order to maximize the profit. Solve the problem graphically.
A firm makes items A and B and the total number of items it can make in a day is 24. It takes one hour to make an item of A and half an hour to make an item of B. The maximum time available per day is 16 hours. The profit on an item of A is Rs 300 and on one item of B is Rs 160. How many items of each type should be produced to maximize the profit? Solve the problem graphically.
A company sells two different products, A and B. The two products are produced in a common production process, which has a total capacity of 500 man-hours. It takes 5 hours to produce a unit of A and 3 hours to produce a unit of B. The market has been surveyed and company officials feel that the maximum number of unit of A that can be sold is 70 and that for B is 125. If the profit is Rs 20 per unit for the product A and Rs 15 per unit for the product B, how many units of each product should be sold to maximize profit?
A box manufacturer makes large and small boxes from a large piece of cardboard. The large boxes require 4 sq. metre per box while the small boxes require 3 sq. metre per box. The manufacturer is required to make at least three large boxes and at least twice as many small boxes as large boxes. If 60 sq. metre of cardboard is in stock, and if the profits on the large and small boxes are Rs 3 and Rs 2 per box, how many of each should be made in order to maximize the total profit?
A library has to accommodate two different types of books on a shelf. The books are 6 cm and 4 cm thick and weigh 1 kg and \[1\frac{1}{2}\] kg each respectively. The shelf is 96 cm long and atmost can support a weight of 21 kg. How should the shelf be filled with the books of two types in order to include the greatest number of books? Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
A factory makes tennis rackets and cricket bats. A tennis racket takes 1.5 hours of machine time and 3 hours of craftman's time in its making while a cricket bat takes 3 hours of machine time and 1 hour of craftman's time. In a day, the factory has the availability of not more than 42 hours of machine time and 24 hours of craftman's time. If the profit on a racket and on a bat is Rs 20 and Rs 10 respectively, find the number of tennis rackets and cricket bats that the factory must manufacture to earn the maximum profit. Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
A cooperative society of farmers has 50 hectares of land to grow two crops X and Y. The profits from crops X and Y per hectare are estimated as ₹10,500 and ₹9,000 respectively. To control weeds, a liquid herbicide has to be used for crops X and Y at the rate of 20 litres and 10 litres per hectare, respectively. Further not more than 800 litres of herbicide should be used in order to protect fish and wildlife using a pond which collects drainage from this land. How much land should be allocated to each crop so as to maximise the total profit of the society?
There are two factories located one at place P and the other at place Q. From these locations, a certain commodity is to be delivered to each of the three depots situated at A, B and C. The weekly requirements of the depots are respectively 5, 5 and 4 units of the commodity while the production capacity of the factories at P and Q are respectively 8 and 6 units. The cost of transportation per unit is given below:
| From \ To | Cost (in ₹) | ||
| A | B | C | |
| P | 160 | 100 | 150 |
| Q | 100 | 120 | 100 |
How many units should be transported from each factory to each depot in order that the transportation cost is minimum. What will be the minimum transportation cost?
The value of objective function is maximum under linear constraints ______.
A company manufactures two types of cardigans: type A and type B. It costs ₹ 360 to make a type A cardigan and ₹ 120 to make a type B cardigan. The company can make at most 300 cardigans and spend at most ₹ 72000 a day. The number of cardigans of type B cannot exceed the number of cardigans of type A by more than 200. The company makes a profit of ₹ 100 for each cardigan of type A and ₹ 50 for every cardigan of type B.
Formulate this problem as a linear programming problem to maximize the profit to the company. Solve it graphically and find the maximum profit.
Find the graphical solution for the system of linear inequation 2x + y ≤ 2, x − y ≤ 1
Draw the graph of inequalities x ≤ 6, y −2 ≤ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 and indicate the feasible region
For the LPP, maximize z = x + 4y subject to the constraints x + 2y ≤ 2, x + 2y ≥ 8, x, y ≥ 0 ______.
The point which provides the solution to the linear programming problem: Max P = 2x + 3y subject to constraints: x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 2x + 2y ≤ 9, 2x + y ≤ 7, x + 2y ≤ 8, is ______
A feasible region in the set of points which satisfy ____________.
The solution set of the inequality 3x + 5y < 4 is ______.
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically:
Minimize: Z = 5x + 10y
Subject to constraints:
x + 2y ≤ 120, x + y ≥ 60, x – 2y ≥ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following Linear Programming problem graphically:
Maximize: Z = 3x + 3.5y
Subject to constraints:
x + 2y ≥ 240,
3x + 1.5y ≥ 270,
1.5x + 2y ≤ 310,
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Maximize: P = 70x + 40y
Subject to: 3x + 2y ≤ 9,
3x + y ≤ 9,
x ≥ 0,y ≥ 0.
The feasible region corresponding to the linear constraints of a Linear Programming Problem is given below.
Which of the following is not a constraint to the given Linear Programming Problem?
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Maximize: z = – x + 2y,
Subject to the constraints: x ≥ 3, x + y ≥ 5, x + 2y ≥ 6, y ≥ 0.
Draw the rough graph and shade the feasible region for the inequalities x + y ≥ 2, 2x + y ≤ 8, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
A linear programming problem is given by Z = px + qy where p, q > 0 subject to the constraints: x + y ≤ 60, 5x + y ≤ 100, x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0
- Solve graphically to find the corner points of the feasible region.
- If Z = px + qy is maximum at (0, 60) and (10, 50), find the relation of p and q. Also mention the number of optimal solution(s) in this case.
