Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A manufacturer of Furniture makes two products : chairs and tables. processing of these products is done on two machines A and B. A chair requires 2 hrs on machine A and 6 hrs on machine B. A table requires 4 hrs on machine A and 2 hrs on machine B. There are 16 hrs of time per day available on machine A and 30 hrs on machine B. Profit gained by the manufacturer from a chair and a table is Rs 3 and Rs 5 respectively. Find with the help of graph what should be the daily production of each of the two products so as to maximize his profit.
उत्तर
Let x chairs and y tables were produced.
Number of chairs and tables cannot be negative.
Therefore, \[x, y \geq 0\]
The given information can be tabulated as follows:
| Time on machine A(hrs) | Time on machine B (hrs) | |
| Chairs | 2 | 6 |
| Tables | 4 | 2 |
| Availability | 16 | 30 |
Therefore, the constraints are
\[2x + 4y \leq 16\]
\[6x + 2y \leq 30\]
Profit gained by the manufacturer from a chair and a table is Rs 3 and Rs 5 respectively. Therefore, profit gained from x chairs and y tables is Rs 3x and Rs 5y.
Total profit = Z = \[3x + 5y\] which is to be maximised
Thus, the mathematical formulation of the given linear programmimg problem is
Max Z = \[3x + 5y\]
subject to
\[2x + 4y \leq 16\]
\[6x + 2y \leq 30\]
First we will convert inequations into equations as follows:
2x + 4y = 16, 6x + 2y =30, x = 0 and y = 0
Region represented by 2x + 4y ≤ 16:
The line 2x + 4y = 16 meets the coordinate axes at A1(8, 0) and B1(0, 4) respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line 2x + 4y = 16. Clearly (0,0) satisfies the 2x + 4y = 16. So, the region which contains the origin represents the solution set of the inequation 2x + 4y ≤ 16.
Region represented by 6x + 2y ≤ 30:
The line 6x + 2y =30 meets the coordinate axes at C1(5, 0) and D1(0, 15) respectively. By joining these points we obtain the line 6x + 2y =30 . Clearly (0,0) satisfies the inequation 6x + 2y ≤ 30. So,the region which contains the origin represents the solution set of the inequation 6x + 2y ≤ 30.
Region represented by x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0:
Since, every point in the first quadrant satisfies these inequations. So, the first quadrant is the region represented by the inequations x ≥ 0, and y ≥ 0.
The feasible region determined by the system of constraints 2x + 4y ≤ 16, 6x + 2y ≤ 30, x ≥ 0, and y ≥ 0 are as follows. The corner points are O(0, 0), B1(0, 4), E1
The corner points are O(0, 0), B1(0, 4), E1
The values of Z at these corner points are as follows
| Corner point | Z= 3x + 5y |
| O | 0 |
| B1 | 20 |
| E1 | 22.2 |
| C1 | 15 |
The maximum value of Z is 22.2 which is attained at B1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Minimize :Z=6x+4y
Subject to : 3x+2y ≥12
x+y ≥5
0 ≤x ≤4
0 ≤ y ≤ 4
A manufacturing company makes two types of teaching aids A and B of Mathematics for class XII. Each type of A requires 9 labour hours for fabricating and 1 labour hour for finishing. Each type of B requires 12 labour hours for fabricating and 3 labour hours for finishing. For fabricating and finishing, the maximum labour hours available per week are 180 and 30, respectively. The company makes a profit of Rs 80 on each piece of type A and Rs 120 on each piece of type B. How many pieces of type A and type B should be manufactured per week to get maximum profit? Make it as an LPP and solve graphically. What is the maximum profit per week?
Solve the following L. P. P. graphically:Linear Programming
Minimize Z = 6x + 2y
Subject to
5x + 9y ≤ 90
x + y ≥ 4
y ≤ 8
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solve the following L.P.P. graphically:
Minimise Z = 5x + 10y
Subject to x + 2y ≤ 120
Constraints x + y ≥ 60
x – 2y ≥ 0 and x, y ≥ 0
Maximize Z = 4x + 3y
subject to
\[3x + 4y \leq 24\]
\[8x + 6y \leq 48\]
\[ x \leq 5\]
\[ y \leq 6\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 2x + 3y
Subject to
\[x + y \geq 1\]
\[10x + y \geq 5\]
\[x + 10y \geq 1\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = −x1 + 2x2
Subject to
\[- x_1 + 3 x_2 \leq 10\]
\[ x_1 + x_2 \leq 6\]
\[ x_1 - x_2 \leq 2\]
\[ x_1 , x_2 \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 3x1 + 4x2, if possible,
Subject to the constraints
\[x_1 - x_2 \leq - 1\]
\[ - x_1 + x_2 \leq 0\]
\[ x_1 , x_2 \geq 0\]
Find the minimum value of 3x + 5y subject to the constraints
− 2x + y ≤ 4, x + y ≥ 3, x − 2y ≤ 2, x, y ≥ 0.
To maintain one's health, a person must fulfil certain minimum daily requirements for the following three nutrients: calcium, protein and calories. The diet consists of only items I and II whose prices and nutrient contents are shown below:
| Food I | Food II | Minimum daily requirement | |
| Calcium Protein Calories |
10 5 2 |
4 6 6 |
20 20 12 |
| Price | Rs 0.60 per unit | Rs 1.00 per unit |
Find the combination of food items so that the cost may be minimum.
A hospital dietician wishes to find the cheapest combination of two foods, A and B, that contains at least 0.5 milligram of thiamin and at least 600 calories. Each unit of Acontains 0.12 milligram of thiamin and 100 calories, while each unit of B contains 0.10 milligram of thiamin and 150 calories. If each food costs 10 paise per unit, how many units of each should be combined at a minimum cost?
One kind of cake requires 300 gm of flour and 15 gm of fat, another kind of cake requires 150 gm of flour and 30 gm of fat. Find the maximum number of cakes which can be made from 7.5 kg of flour and 600 gm of fat, assuming that there is no shortage of the other ingradients used in making the cake. Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
A dietician wishes to mix together two kinds of food X and Y in such a way that the mixture contains at least 10 units of vitamin A, 12 units of vitamin B and 8 units of vitamin C. The vitamin contents of one kg food is given below:
| Food | Vitamin A | Vitamin B | Vitamin C |
| X | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Y | 2 | 2 | 1 |
One kg of food X costs ₹16 and one kg of food Y costs ₹20. Find the least cost of the mixture which will produce the required diet?
A factory manufactures two types of screws, A and B, each type requiring the use of two machines - an automatic and a hand-operated. It takes 4 minute on the automatic and 6 minutes on the hand-operated machines to manufacture a package of screws 'A', while it takes 6 minutes on the automatic and 3 minutes on the hand-operated machine to manufacture a package of screws 'B'. Each machine is available for at most 4 hours on any day. The manufacturer can sell a package of screws 'A' at a profit of 70 P and screws 'B' at a profit of Rs 1. Assuming that he can sell all the screws he can manufacture, how many packages of each type should the factory owner produce in a day in order to maximize his profit? Determine the maximum profit.
A company manufactures two types of toys A and B. Type A requires 5 minutes each for cutting and 10 minutes each for assembling. Type B requires 8 minutes each for cutting and 8 minutes each for assembling. There are 3 hours available for cutting and 4 hours available for assembling in a day. The profit is Rs 50 each on type A and Rs 60 each on type B. How many toys of each type should the company manufacture in a day to maximize the profit?
A company sells two different products, A and B. The two products are produced in a common production process, which has a total capacity of 500 man-hours. It takes 5 hours to produce a unit of A and 3 hours to produce a unit of B. The market has been surveyed and company officials feel that the maximum number of unit of A that can be sold is 70 and that for B is 125. If the profit is Rs 20 per unit for the product A and Rs 15 per unit for the product B, how many units of each product should be sold to maximize profit?
A box manufacturer makes large and small boxes from a large piece of cardboard. The large boxes require 4 sq. metre per box while the small boxes require 3 sq. metre per box. The manufacturer is required to make at least three large boxes and at least twice as many small boxes as large boxes. If 60 sq. metre of cardboard is in stock, and if the profits on the large and small boxes are Rs 3 and Rs 2 per box, how many of each should be made in order to maximize the total profit?
A small firm manufactures gold rings and chains. The total number of rings and chains manufactured per day is at most 24. It takes 1 hour to make a ring and 30 minutes to make a chain. The maximum number of hours available per day is 16. If the profit on a ring is Rs 300 and that on a chain is Rs 190, find the number of rings and chains that should be manufactured per day, so as to earn the maximum profit. Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
A merchant plans to sell two types of personal computers a desktop model and a portable model that will cost Rs 25,000 and Rs 40,000 respectively. He estimates that the total monthly demand of computers will not exceed 250 units. Determine the number of units of each type of computers which the merchant should stock to get maximum profit if he does not want to invest more than Rs 70 lakhs and his profit on the desktop model is Rs 4500 and on the portable model is Rs 5000. Make an LPP and solve it graphically.
A small firm manufactures necklaces and bracelets. The total number of necklaces and bracelets that it can handle per day is at most 24. It takes one hour to make a bracelet and half an hour to make a necklace. The maximum number of hours available per day is 16. If the profit on a necklace is Rs 100 and that on a bracelet is Rs 300. Formulate on L.P.P. for finding how many of each should be produced daily to maximize the profit?
It is being given that at least one of each must be produced.
A company manufactures two types of novelty souvenirs made of plywood. Souvenirs of type A
require 5 minutes each for cutting and 10 minutes each for assembling. Souvenirs of type B require 8 minutes each for cutting and 8 minutes each for assembling. There are 3 hours and 20 minutes available for cutting and 4 hours available for assembling. The profit is Rs. 50 each for type A and Rs. 60 each for type B souvenirs. How many souvenirs of each type should the company manufacture in order to maximize profit? Formulate the above LPP and solve it graphically and also find the maximum profit.
A farmer has a supply of chemical fertilizer of type A which contains 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and of type B which contains 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After the soil test, it is found that at least 7 kg of nitrogen and the same quantity of phosphoric acid is required for a good crop. The fertilizer of type A costs ₹ 5.00 per kg and the type B costs ₹ 8.00 per kg. Using Linear programming, find how many kilograms of each type of fertilizer should be bought to meet the requirement and for the cost to be minimum. Find the feasible region in the graph.
A company manufactures two types of products A and B. Each unit of A requires 3 grams of nickel and 1 gram of chromium, while each unit of B requires 1 gram of nickel and 2 grams of chromium. The firm can produce 9 grams of nickel and 8 grams of chromium. The profit is ₹ 40 on each unit of the product of type A and ₹ 50 on each unit of type B. How many units of each type should the company manufacture so as to earn a maximum profit? Use linear programming to find the solution.
Find the graphical solution for the system of linear inequation 2x + y ≤ 2, x − y ≤ 1
Find the feasible solution of linear inequation 2x + 3y ≤ 12, 2x + y ≤ 8, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 by graphically
Maximise and Minimise Z = 3x – 4y subject to x – 2y ≤ 0, – 3x + y ≤ 4, x – y ≤ 6, x, y ≥ 0
A set of values of decision variables which satisfies the linear constraints and nn-negativity conditions of an L.P.P. is called its ____________.
Z = 20x1 + 20x2, subject to x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0, x1 + 2x2 ≥ 8, 3x1 + 2x2 ≥ 15, 5x1 + 2x2 ≥ 20. The minimum value of Z occurs at ____________.
Let R be the feasible region (convex polygon) for a linear programming problem and let Z = ax + by be the objective function. When Z has an optimal value (maximum or minimum), where the variables x and y are subject to constraints described by linear inequalities,
Let R be the feasible region for a linear programming problem, and let Z = ax + by be the objective function. If R is bounded, then ____________.
Minimise z = – 3x + 4y subject to x + 2y ≤ 8, 3x + 2y ≤ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 What will be the minimum value of z ?
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Maximize Z = 400x + 300y subject to x + y ≤ 200, x ≤ 40, x ≥ 20, y ≥ 0
The maximum value of 2x + y subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 26 and 5x + 3y ≤ 30, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The corner points of the feasible region of a linear programming problem are (0, 4), (8, 0) and `(20/3, 4/3)`. If Z = 30x + 24y is the objective function, then (maximum value of Z – minimum value of Z) is equal to ______.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Minimize: Z = 60x + 80y
Subject to constraints:
3x + 4y ≥ 8
5x + 2y ≥ 11
x, y ≥ 0
The feasible region corresponding to the linear constraints of a Linear Programming Problem is given below.
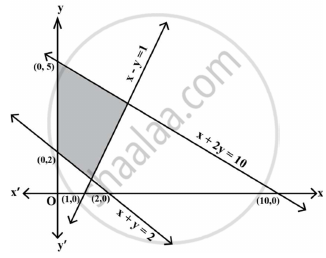
Which of the following is not a constraint to the given Linear Programming Problem?
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Maximize: z = – x + 2y,
Subject to the constraints: x ≥ 3, x + y ≥ 5, x + 2y ≥ 6, y ≥ 0.
Minimize z = x + 2y,
Subject to x + 2y ≥ 50, 2x – y ≤ 0, 2x + y ≤ 100, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
