Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically:
Minimize z = 6 x + 3 y
Subject to the constraints:
4 x + \[y \geq\] 80
x + 5 \[y \geq\] 115
3 x + 2 \[y \leq\] 150
\[x \geq\] 0 , \[y \geq\] 0
उत्तर
The given constraints are
4x + y \[\geq\] 80
x + 5y \[\geq\] 115
3x + 2y \[\geq\] 150
x,y \[\geq\] 0
Converting the given inequations into equations, we get
4x + y = 80, x + 5y = 115, 3x + 2y = 150, x = 0 and y = 0
These lines are drawn on the graph and the shaded region ABC represents the feasible region of the given LPP.

It can be observed that the feasible region is bounded. The coordinates of the corner points of the feasible region are A(2, 72), B(15, 20) and C(40, 15).
The values of the objective function, Z at these corner points are given in the following table:
| Corner Point | Value of the Objective Function Z = 6x + 3y |
| A(2, 72) | Z = 6 × 2 + 3 × 72 = 228 |
| B(15, 20) | Z = 6 × 15 + 3 × 20 = 150 |
| C(40, 15) | Z = 6 × 40 + 3 × 15 = 285 |
From the table, Z is minimum at x = 15 and y = 20 and the minimum value of Z is 150.
Thus, the minimum value of Z is 150.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A manufacturer produces two products A and B. Both the products are processed on two different machines. The available capacity of first machine is 12 hours and that of second machine is 9 hours per day. Each unit of product A requires 3 hours on both machines and each unit of product B requires 2 hours on first machine and 1 hour on second machine. Each unit of product A is sold at Rs 7 profit and B at a profit of Rs 4. Find the production level per day for maximum profit graphically.
Solve the following linear programming problem graphically :
Maximise Z = 7x + 10y subject to the constraints
4x + 6y ≤ 240
6x + 3y ≤ 240
x ≥ 10
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Solve the following L.P.P. graphically:
Minimise Z = 5x + 10y
Subject to x + 2y ≤ 120
Constraints x + y ≥ 60
x – 2y ≥ 0 and x, y ≥ 0
A dietician wishes to mix two kinds ·of food X· and Y in such a way that the mixture contains at least 10 units of vitamin A, 12 units of vitamin B arid 8 units of vitamin C. The vitamin contents of one kg food is given below:
| Food | Vitamin A | Vitamin.B | Vitamin C |
| X | 1 unit | 2 unit | 3 unit |
| Y | 2 unit | 2 unit | 1 unit |
Orie kg of food X costs Rs 24 and one kg of food Y costs Rs 36. Using Linear Programming, find the least cost of the total mixture. which will contain the required vitamins.
Maximise z = 8x + 9y subject to the constraints given below :
2x + 3y ≤ 6
3x − 2y ≤6
y ≤ 1
x, y ≥ 0
A diet for a sick person must contain at least 4000 units of vitamins, 50 units of minerals and 1400 of calories. Two foods A and B, are available at a cost of Rs 4 and Rs 3 per unit respectively. If one unit of A contains 200 units of vitamin, 1 unit of mineral and 40 calories and one unit of food B contains 100 units of vitamin, 2 units of minerals and 40 calories, find what combination of foods should be used to have the least cost?
Reshma wishes to mix two types of food P and Q in such a way that the vitamin contents of the mixture contains at least 8 units of vitamin A and 11 units of vitamin B. Food P costs ₹60/kg and food Q costs ₹80/kg. Food P contains 3 units/kg of vitamin A and 5 units/kg of vitamin B while food Q contains 4 units/kg of vitamin A and 2 units/kg of vitamin B. Determine the minimum cost of the mixture.
If a young man drives his vehicle at 25 km/hr, he has to spend Rs 2 per km on petrol. If he drives it at a faster speed of 40 km/hr, the petrol cost increases to Rs 5/per km. He has Rs 100 to spend on petrol and travel within one hour. Express this as an LPP and solve the same.
A manufacturer makes two types A and B of tea-cups. Three machines are needed for the manufacture and the time in minutes required for each cup on the machines is given below:
| Machines | |||
| I | II | III | |
| A B |
12 6 |
18 0 |
6 9 |
Each machine is available for a maximum of 6 hours per day. If the profit on each cup A is 75 paise and that on each cup B is 50 paise, show that 15 tea-cups of type A and 30 of type B should be manufactured in a day to get the maximum profit.
A firm manufacturing two types of electric items, A and B, can make a profit of Rs 20 per unit of A and Rs 30 per unit of B. Each unit of A requires 3 motors and 4 transformers and each unit of B requires 2 motors and 4 transformers. The total supply of these per month is restricted to 210 motors and 300 transformers. Type B is an export model requiring a voltage stabilizer which has a supply restricted to 65 units per month. Formulate the linear programing problem for maximum profit and solve it graphically.
A gardener has supply of fertilizer of type I which consists of 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and type II fertilizer which consists of 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, he finds that he needs at least 14 kg of nitrogen and 14 kg of phosphoric acid for his crop. If the type I fertilizer costs 60 paise per kg and type II fertilizer costs 40 paise per kg, determine how many kilograms of each fertilizer should be used so that nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost. What is the minimum cost?
A firm manufactures two types of products A and B and sells them at a profit of Rs 5 per unit of type A and Rs 3 per unit of type B. Each product is processed on two machines M1 and M2. One unit of type A requires one minute of processing time on M1 and two minutes of processing time on M2, whereas one unit of type B requires one minute of processing time on M1 and one minute on M2. Machines M1 and M2 are respectively available for at most 5 hours and 6 hours in a day. Find out how many units of each type of product should the firm produce a day in order to maximize the profit. Solve the problem graphically.
A box manufacturer makes large and small boxes from a large piece of cardboard. The large boxes require 4 sq. metre per box while the small boxes require 3 sq. metre per box. The manufacturer is required to make at least three large boxes and at least twice as many small boxes as large boxes. If 60 sq. metre of cardboard is in stock, and if the profits on the large and small boxes are Rs 3 and Rs 2 per box, how many of each should be made in order to maximize the total profit?
A small firm manufactures gold rings and chains. The total number of rings and chains manufactured per day is at most 24. It takes 1 hour to make a ring and 30 minutes to make a chain. The maximum number of hours available per day is 16. If the profit on a ring is Rs 300 and that on a chain is Rs 190, find the number of rings and chains that should be manufactured per day, so as to earn the maximum profit. Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
A library has to accommodate two different types of books on a shelf. The books are 6 cm and 4 cm thick and weigh 1 kg and \[1\frac{1}{2}\] kg each respectively. The shelf is 96 cm long and atmost can support a weight of 21 kg. How should the shelf be filled with the books of two types in order to include the greatest number of books? Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
A factory makes tennis rackets and cricket bats. A tennis racket takes 1.5 hours of machine time and 3 hours of craftman's time in its making while a cricket bat takes 3 hours of machine time and 1 hour of craftman's time. In a day, the factory has the availability of not more than 42 hours of machine time and 24 hours of craftman's time. If the profit on a racket and on a bat is Rs 20 and Rs 10 respectively, find the number of tennis rackets and cricket bats that the factory must manufacture to earn the maximum profit. Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
There are two types of fertilizers F1 and F2. F1 consists of 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and F2 consists of 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, a farmer finds the she needs atleast 14 kg of nitrogen and 14 kg of phosphoric acid for her crop. If F1 costs ₹6/kg and F2 costs ₹5/kg, determine how much of each type of fertilizer should be used so that the nutrient requirements are met at minimum cost. What is the minimum cost?
There are two factories located one at place P and the other at place Q. From these locations, a certain commodity is to be delivered to each of the three depots situated at A, B and C. The weekly requirements of the depots are respectively 5, 5 and 4 units of the commodity while the production capacity of the factories at P and Q are respectively 8 and 6 units. The cost of transportation per unit is given below:
| From \ To | Cost (in ₹) | ||
| A | B | C | |
| P | 160 | 100 | 150 |
| Q | 100 | 120 | 100 |
How many units should be transported from each factory to each depot in order that the transportation cost is minimum. What will be the minimum transportation cost?
The value of objective function is maximum under linear constraints ______.
Maximize: z = 3x + 5y Subject to
x +4y ≤ 24 3x + y ≤ 21
x + y ≤ 9 x ≥ 0 , y ≥0
A farmer has a supply of chemical fertilizer of type A which contains 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and of type B which contains 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After the soil test, it is found that at least 7 kg of nitrogen and the same quantity of phosphoric acid is required for a good crop. The fertilizer of type A costs ₹ 5.00 per kg and the type B costs ₹ 8.00 per kg. Using Linear programming, find how many kilograms of each type of fertilizer should be bought to meet the requirement and for the cost to be minimum. Find the feasible region in the graph.
The graph of the inequality 3X − 4Y ≤ 12, X ≤ 1, X ≥ 0, Y ≥ 0 lies in fully in
Find the feasible solution of linear inequation 2x + 3y ≤ 12, 2x + y ≤ 8, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 by graphically
Draw the graph of inequalities x ≤ 6, y −2 ≤ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 and indicate the feasible region
Area of the region bounded by y = cos x, x = 0, x = π and X-axis is ______ sq.units.
If 4x + 5y ≤ 20, x + y ≥ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, maximum 2x + 3y is ______.
The maximum of z = 5x + 2y, subject to the constraints x + y ≤ 7, x + 2y ≤ 10, x, y ≥ 0 is ______.
In linear programming feasible region (or solution region) for the problem is ____________.
Let R be the feasible region for a linear programming problem, and let Z = ax + by be the objective function. If R is bounded, then the objective function Z has both a maximum and a minimum value on R and ____________.
The feasible region (shaded) for a L.P.P is shown in the figure. The maximum Z = 5x + 7y is ____________.
Which of the statements describe the solution set for `-2(x + 8) = - 2x + 20`?
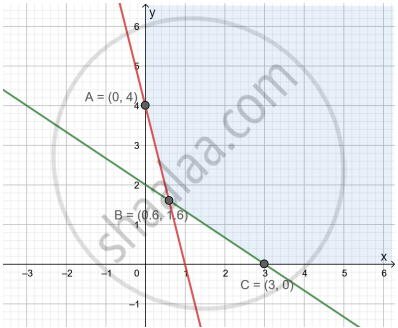
The corner points of the shaded unbounded feasible region of an LPP are (0, 4), (0.6, 1.6) and (3, 0) as shown in the figure. The minimum value of the objective function Z = 4x + 6y occurs at ______.
The maximum value of z = 5x + 2y, subject to the constraints x + y ≤ 7, x + 2y ≤ 10, x, y ≥ 0 is ______.
Solve the following Linear Programming problem graphically:
Maximize: Z = 3x + 3.5y
Subject to constraints:
x + 2y ≥ 240,
3x + 1.5y ≥ 270,
1.5x + 2y ≤ 310,
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Maximize: P = 70x + 40y
Subject to: 3x + 2y ≤ 9,
3x + y ≤ 9,
x ≥ 0,y ≥ 0.
Draw the rough graph and shade the feasible region for the inequalities x + y ≥ 2, 2x + y ≤ 8, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Aman has ₹ 1500 to purchase rice and wheat for his grocery shop. Each sack of rice and wheat costs ₹ 180 and Rupee ₹ 120 respectively. He can store a maximum number of 10 bags in his shop. He will earn a profit of ₹ 11 per bag of rice and ₹ 9 per bag of wheat.
- Formulate a Linear Programming Problem to maximise Aman’s profit.
- Calculate the maximum profit.
