Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Maximum deviation from ideal gas is expected from
पर्याय
\[\ce{CH4_{(g)}}\]
\[\ce{NH3_{(g)}}\]
\[\ce{H2_{(g)}}\]
\[\ce{N2_{(g)}}\]
उत्तर
\[\ce{NH3_{(g)}}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The value of the universal gas constant depends upon
Compressibility factor for CO2 at 400 K and 71.0 bar is 0.8697. The molar volume of CO2 under these conditions is
Explain whether a gas approaches ideal behavior or deviates from ideal behaviour if it is compressed to a smaller volume at a constant temperature.
Which of the following gases would you expect to deviate from ideal behavior under conditions of low-temperature F2, Cl2, or Br2? Explain.
A plot of volume (V) versus temperature (T) for a gas at constant pressure is a straight line passing through the origin. The plots at different values of pressure are shown in Figure. Which of the following order of pressure is correct for this gas?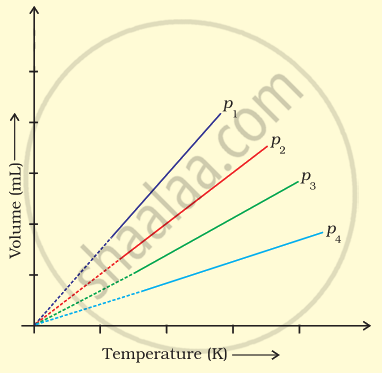
If 1 gram of each of the following gases are taken at STP, which of the gases will occupy (a) greatest volume and (b) smallest volume?
\[\ce{CO, H2O, CH4 , NO}\]
Compressibility factor, Z, of a gas is given as Z = `(pV)/(nRT)`. What is the value of Z for an ideal gas?
Compressibility factor, Z, of a gas is given as Z = `(pV)/(nRT)`. For real gas what will be the effect on value of Z above Boyle’s temperature?
Assertion (A): At constant temperature, pV vs V plot for real gases is not a straight line.
Reason (R): At high pressure all gases have \[\ce{Z}\] > 1 but at intermediate pressure most gases have \[\ce{Z}\] < 1.
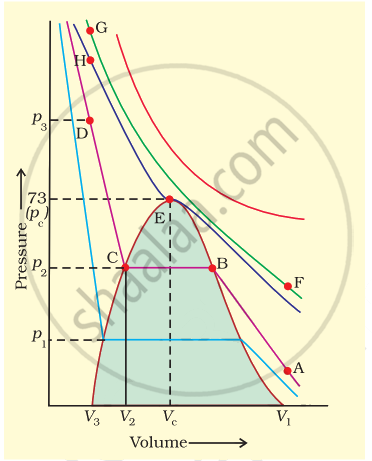
Isotherms of carbon dioxide gas are shown in figure. Mark a path for changing gas into liquid such that only one phase (i.e., either a gas or a liquid) exists at any time during the change. Explain how the temperature, volume and pressure should be changed to carry out the change.