Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The weight of an object is more at the poles than at the equator. Is it beneficial to purchase goods at equator and sell them at the pole? Does it matter whether a spring balance is used or an equal-beam balance is used?
उत्तर
The weight of an object is more at the poles than that at the equator. In purchasing or selling goods, we measure the mass of the goods. The balance used to measure the mass is calibrated according to the place to give its correct reading. So, it is not beneficial to purchase goods at the equator and sell them at the poles. A beam balance measures the mass of an object, so it can be used here. For using a spring balance, we need to calibrate it according to the place to give the correct readings.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write the formula to find the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and an object on the surface of the earth.
What happens to the force between two objects, if the mass of one object is doubled?
What happens to the force between two objects, if the masses of both objects are doubled?
Answer the following:
You can shield a charge from electrical forces by putting it inside a hollow conductor. Can you shield a body from the gravitational influence of nearby matter by putting it inside a hollow sphere or by some other means?
Can we apply Newton’s third law to the gravitational force ? Explain your answer.
State the universal law of gravitation. Name the scientist who gave this law.
Suppose the gravitational potential due to a small system is k/r2 at a distance r from it. What will be the gravitational field? Can you think of any such system? What happens if there were negative masses?
Two small bodies of masses 10 kg and 20 kg are kept a distance 1.0 m apart and released. Assuming that only mutual gravitational forces are acting, find the speeds of the particles when the separation decreases to 0.5 m.
Derive an expression for the gravitational field due to a uniform rod of length L and mass M at a point on its perpendicular bisector at a distance d from the centre.
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. It goes to a height 20 m and then returns to the ground. Taking acceleration due to gravity g to be 10 ms-2, find: the initial velocity of the ball.
All objects in the universe attract each other along the line joining their________.
At what height above the earth's surface would the value of acceleration due to gravity be half of what it is on the surface? Take the radius of earth to be R.
What does a force do in the following case?
You twist a piece of rubber.
What does a force do in the following case?
You catch a kicked ball.
Is there a gravitational attraction between you and the book? Explain.
Solve the following problem.
Find the gravitational force between the Sun and the Earth.
Given Mass of the Sun = 1.99 × 1030 kg
Mass of the Earth = 5.98 × 1024 kg
The average distance between the Earth and the Sun = 1.5 × 1011 m.
The value of universal gravitational constant (G) in the SI unit is ______.
Molecules in air in the atmosphere are attracted by gravitational force of the earth. Explain why all of them do not fall into the earth just like an apple falling from a tree.
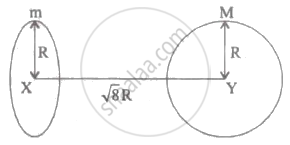
Find the gravitational force of attraction between the ring and sphere as shown in the diagram, where the plane of the ring is perpendicular to the line joining the centres. If `sqrt8` R is the distance between the centres of a ring (of mass 'm')and a sphere (mass 'M') where both have equal radius 'R'.