Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show that P(– 2, 2), Q(2, 2) and R(2, 7) are vertices of a right angled triangle
उत्तर
Distance between two points = `sqrt((x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2`
By distance formula,
PQ = `sqrt([2 - (-2)]^2 + (2 - 2)^2`
= `sqrt((2 + 2)^2 + (0)^2`
= `sqrt((4)^2`
= 4 .....(i)
QR = `sqrt((2 - 2)^2 + (7 - 2)^2`
= `sqrt((0)^2 + (5)^2`
= `sqrt((5)^2`
= 5 ......(ii)
PR = `sqrt([2 -(-2)]^2 + (7 - 2)^2`
= `sqrt((2 + 2)^2 + (5)^2`
= `sqrt((4)^2 + (5)^2`
= `sqrt(16 + 25)`
= `sqrt(41)`
Now, PR2 = `(sqrt(41))^2` = 41 ......(iii)
Consider, PQ2 + QR2
= 42 + 52
= 16 + 25
= 41 ......[From (i) and (ii)]
∴ PR2 = PQ2 + QR2 ......[From (iii)]
∴ ∆PQR is a right angled triangle. ......[Converse of Pythagoras theorem]
∴ Points P, Q, and R are the vertices of a right angled triangle.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the distance between the following pairs of points:
(2, 3), (4, 1)
Find the distance between the following pairs of points:
(−5, 7), (−1, 3)
An equilateral triangle has two vertices at the points (3, 4) and (−2, 3), find the coordinates of the third vertex.
Find the centre of the circle passing through (6, -6), (3, -7) and (3, 3)
Two opposite vertices of a square are (-1, 2) and (3, 2). Find the coordinates of other two
vertices.
Find the distance between the following pairs of point.
W `((- 7)/2 , 4)`, X (11, 4)
Determine whether the points are collinear.
A(1, −3), B(2, −5), C(−4, 7)
Find the distances between the following point.
A(a, 0), B(0, a)
Find the distances between the following point.
P(–6, –3), Q(–1, 9)
Find the distance of the following point from the origin :
(0 , 11)
Prove that the points (0 , -4) , (6 , 2) , (3 , 5) and (-3 , -1) are the vertices of a rectangle.
Find the distance of the following points from origin.
(a+b, a-b)
Use distance formula to show that the points A(-1, 2), B(2, 5) and C(-5, -2) are collinear.
If the length of the segment joining point L(x, 7) and point M(1, 15) is 10 cm, then the value of x is ______
If the distance between point L(x, 7) and point M(1, 15) is 10, then find the value of x
Show that the point (11, – 2) is equidistant from (4, – 3) and (6, 3)
AOBC is a rectangle whose three vertices are A(0, 3), O(0, 0) and B(5, 0). The length of its diagonal is ______.
∆ABC with vertices A(–2, 0), B(2, 0) and C(0, 2) is similar to ∆DEF with vertices D(–4, 0), E(4, 0) and F(0, 4).
Name the type of triangle formed by the points A(–5, 6), B(–4, –2) and C(7, 5).
Read the following passage:
|
Alia and Shagun are friends living on the same street in Patel Nagar. Shagun's house is at the intersection of one street with another street on which there is a library. They both study in the same school and that is not far from Shagun's house. Suppose the school is situated at the point O, i.e., the origin, Alia's house is at A. Shagun's house is at B and library is at C. |
Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
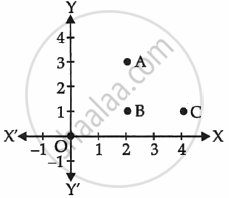
- How far is Alia's house from Shagun's house?
- How far is the library from Shagun's house?
- Show that for Shagun, school is farther compared to Alia's house and library.
OR
Show that Alia’s house, shagun’s house and library for an isosceles right triangle.
