Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Pythagoras Theorem
3: Circle
4: Geometric Constructions
▶ 5: Co-ordinate Geometry
6: Trigonometry
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 5 - Co-ordinate Geometry SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 5 - Co-ordinate Geometry - Shaalaa.com](/images/geometry-mathematics-2-english-10-standard-ssc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 5: Co-ordinate Geometry
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 5 of Maharashtra State Board SCERT Maharashtra for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Co-ordinate Geometry Q.1 (A)
MCQ [1 Mark]
Point P is midpoint of segment AB where A(– 4, 2) and B(6, 2), then the coordinates of P are ______
(–1, 2)
(1, 2)
(1, –2)
(–1, 2)
The distance between point P(2, 2) and Q(5, x) is 5 cm, then the value of x ______
2
6
3
1
The distance between points P(–1, 1) and Q(5, –7) is ______
11 cm
10 cm
5 cm
7 cm
If the length of the segment joining point L(x, 7) and point M(1, 15) is 10 cm, then the value of x is ______
7
7 or – 5
–1
1
Find distance between point A(– 3, 4) and origin O
7 cm
10 cm
5 cm
– 5cm
If point P(1, 1) divide segment joining point A and point B(–1, –1) in the ratio 5 : 2, then the coordinates of A are ______
(3, 3)
(6, 6)
(2, 2)
(1, 1)
If segment AB is parallel Y-axis and coordinates of A are (1, 3), then the coordinates of B are ______
(3, 1)
(5, 3)
(3, 0)
(1, – 3)
If point P is midpoint of segment joining point A(– 4, 2) and point B(6, 2), then the coordinates of P are ______
(–1, 2)
(1, 2)
(1, –2)
(–1, –2)
If point P divides segment AB in the ratio 1 : 3 where A(– 5, 3) and B(3, – 5), then the coordinates of P are ______
(– 2, – 2)
(– 1, – 1)
(– 3, 1)
(1, – 3)
If the sum of X-coordinates of the vertices of a triangle is 12 and the sum of Y-coordinates is 9, then the coordinates of centroid are ______
(12, 9)
(9, 12)
(4, 3)
(3, 4)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Co-ordinate Geometry Q.1 (B)
Solve the following [1 Mark]
Find the coordinates of the point of intersection of the graph of the equation x = 2 and y = – 3
Find distance between point A(7, 5) and B(2, 5)
The coordinates of diameter AB of a circle are A(2, 7) and B(4, 5), then find the coordinates of the centre
Write the X-coordinate and Y-coordinate of point P(– 5, 4)
What are the coordinates of origin?
Find distance of point A(6, 8) from origin
Find coordinates of midpoint of segment joining (– 2, 6) and (8, 2)
Find the coordinates of centroid of a triangle whose vertices are (4, 7), (8, 4) and (7, 11)
Find distance between points O(0, 0) and B(– 5, 12)
Find coordinates of midpoint of the segment joining points (0, 2) and (12, 14)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Co-ordinate Geometry Q.2 (A)
Complete the activity [2 Marks]
Find distance between point Q(3, – 7) and point R(3, 3)
Solution: Suppose Q(x1, y1) and point R(x2, y2)
x1 = 3, y1 = – 7 and x2 = 3, y2 = 3
Using distance formula,
d(Q, R) = `sqrt(square)`
∴ d(Q, R) = `sqrt(square - 100)`
∴ d(Q, R) = `sqrt(square)`
∴ d(Q, R) = `square`
Find distance between point A(–1, 1) and point B(5, –7):
Solution: Suppose A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2)
x1 = –1, y1 = 1 and x2 = 5, y2 = – 7
Using distance formula,
d(A, B) = `sqrt((x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2`
∴ d(A, B) = `sqrt(square +[(-7) + square]^2`
∴ d(A, B) = `sqrt(square)`
∴ d(A, B) = `square`
Find coordinates of the midpoint of a segment joining point A(–1, 1) and point B(5, –7)
Solution: Suppose A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2)
x1 = –1, y1 = 1 and x2 = 5, y2 = –7
Using midpoint formula,
∴ Coordinates of midpoint of segment AB
= `((x_1 + x_2)/2, (y_1+ y_2)/2)`
= `(square/2, square/2)`
∴ Coordinates of the midpoint = `(4/2, square/2)`
∴ Coordinates of the midpoint = `(2, square)`
The coordinates of the vertices of a triangle ABC are A (–7, 6), B(2, –2) and C(8, 5). Find coordinates of its centroid.
Solution: Suppose A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2) and C(x3, y3)
x1 = –7, y1 = 6 and x2 = 2, y2 = –2 and x3 = 8, y3 = 5
Using Centroid formula
∴ Coordinates of the centroid of a traingle
ABC = `((x_1 + x_2 + x_3)/3, (y_1 + y_2 + y_3)/3)`
= `(square/3, square/3)`
∴ Coordinates of the centroid of a triangle ABC = `(3/3, square)`
∴ Coordinates of the centroid of a triangle ABC = `(1 , square)`
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Co-ordinate Geometry Q.2 (B)
Solve [2 Marks]
The point Q divides segment joining A(3, 5) and B(7, 9) in the ratio 2 : 3. Find the X-coordinate of Q
If the distance between point L(x, 7) and point M(1, 15) is 10, then find the value of x
Find the coordinates of midpoint of segment joining (22, 20) and (0, 16)
Find distance CD where C(– 3a, a), D(a, – 2a)
Show that the point (11, – 2) is equidistant from (4, – 3) and (6, 3)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Co-ordinate Geometry Q.3 (A)
Complete the activity [3 Marks]
If the point P (6, 7) divides the segment joining A(8, 9) and B(1, 2) in some ratio, find that ratio
Solution:
Point P divides segment AB in the ratio m: n.
A(8, 9) = (x1, y1), B(1, 2 ) = (x2, y2) and P(6, 7) = (x, y)
Using Section formula of internal division,
∴ 7 = `("m"(square) - "n"(9))/("m" + "n")`
∴ 7m + 7n = `square` + 9n
∴ 7m – `square` = 9n – `square`
∴ `square` = 2n
∴ `"m"/"n" = square`
From the figure given alongside, find the length of the median AD of triangle ABC. Complete the activity.
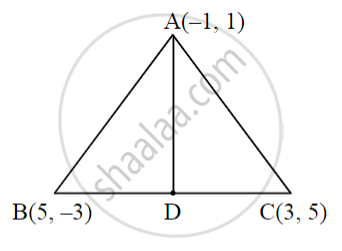
Solution:
Here A(–1, 1), B(5, – 3), C(3, 5) and suppose D(x, y) are coordinates of point D.
Using midpoint formula,
x = `(5 + 3)/2`
∴ x = `square`
y = `(-3 + 5)/2`
∴ y = `square`
Using distance formula,
∴ AD = `sqrt((4 - square)^2 + (1 - 1)^2`
∴ AD = `sqrt((square)^2 + (0)^2`
∴ AD = `sqrt(square)`
∴ The length of median AD = `square`
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Co-ordinate Geometry Q.3 (B)
Solve the following [3 Marks]
Show that P(– 2, 2), Q(2, 2) and R(2, 7) are vertices of a right angled triangle
Show that the point (0, 9) is equidistant from the points (– 4, 1) and (4, 1)
Point P(– 4, 6) divides point A(– 6, 10) and B(m, n) in the ratio 2:1, then find the coordinates of point B
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Co-ordinate Geometry Q.4
Solve [4 Marks]
Show that points A(– 4, –7), B(–1, 2), C(8, 5) and D(5, – 4) are the vertices of a parallelogram ABCD
Show that the points (0, –1), (8, 3), (6, 7) and (– 2, 3) are vertices of a rectangle.
Show that the points (2, 0), (– 2, 0) and (0, 2) are vertices of a triangle. State the type of triangle with reason
If A(5, 4), B(–3, –2) and C(1, –8) are the vertices of a ∆ABC. Segment AD is median. Find the length of seg AD:
Show that A(1, 2), (1, 6), C(1 + 2 `sqrt(3)`, 4) are vertices of a equilateral triangle
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC 5 Co-ordinate Geometry Q.5
Solve [3 Marks]
Seg OA is the radius of a circle with centre O. The coordinates of point A is (0, 2) then decide whether the point B(1, 2) is on the circle?
Find the ratio in which Y-axis divides the point A(3, 5) and point B(– 6, 7). Find the coordinates of the point
The points (7, – 6), (2, k) and (h, 18) are the vertices of triangle. If (1, 5) are the coordinates of centroid, find the value of h and k
Using distance formula decide whether the points (4, 3), (5, 1), and (1, 9) are collinear or not.
Solutions for 5: Co-ordinate Geometry
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 5 - Co-ordinate Geometry SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 5 - Co-ordinate Geometry - Shaalaa.com](/images/geometry-mathematics-2-english-10-standard-ssc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 5 - Co-ordinate Geometry
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board 5 (Co-ordinate Geometry) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. SCERT Maharashtra textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC chapter 5 Co-ordinate Geometry are Distance Formula, Division of a Line Segment, Coordinate Geometry, Intercepts Made by a Line, Slope of a Line, General Equation of a Line, Standard Forms of Equation of a Line, The Mid-point of a Line Segment (Mid-point Formula), Section Formula, Centroid Formula.
Using SCERT Maharashtra Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC solutions Co-ordinate Geometry exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in SCERT Maharashtra Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC students prefer SCERT Maharashtra Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 5, Co-ordinate Geometry Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC additional questions for Mathematics Geometry (Mathematics 2) [English] 10 Standard SSC Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
