Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show that the time required for 99.9% completion of a first-order reaction is three times the time required for 90% completion.
उत्तर
For a first-order reaction,
`"t" = 2.303/"k" "log"_10 ["A"]_0/["A"]_"t"`
i. Time is taken for 99.9% completion:
Let the time taken for 99.9% completion of the reaction be t99.9%.
Let initial concentration, [A]0 = a
The final concentration, [A]t = a - 99.9% of a
= `"a" - (99.9/100 xx "a") = 0.001 "a"`
t99.9% = `2.303/"k" "log"_10 ["A"]_0/["A"]_"t"`
= `2.303/"k" "log"_10 "a"/(0.001 "a")`
= `2.303/"k" "log"_10 1000` ...(1)
ii. Time is taken for 90% completion:
Let the time taken for 90% completion of the reaction be t90%.
Let initial concentration, [A]0 = a
Then, final concentration, [A]t = a - 90% of a
= a - `(90/100 xx "a") = 0.1 "a"`
t90% = `2.303/"k" "log"_10 ["A"]_0/["A"]_"t" = 2.303/"k" "log"_10 "a"/(0.1 "a")`
= `2.303/"k" "log"_10 10` ...(2)
Dividing (1) by (2), we get
`("t"_99.9%)/("t"_90%) = (2.303/"k" "log"_10 1000)/(2.303/"k" "log"_10 10) = ("log"_10 1000)/("log"_10 10) = 3/1`
∴ `("t"_99.9%)/("t"_90%) = 3`
∴ t99.9% = 3 t90%
Therefore, for a first-order reaction, the time required for 99.9% completion is 3 times that required for 90% completion.
संबंधित प्रश्न
A first order reaction has a rate constant 1.15 × 10−3 s−1. How long will 5 g of this reactant take to reduce to 3 g?
The rate constant for a first order reaction is 60 s−1. How much time will it take to reduce the initial concentration of the reactant to its `1/16`th value?
For the decomposition of azoisopropane to hexane and nitrogen at 543 K, the following data are obtained.
| t (sec) | P(mm of Hg) |
| 0 | 35.0 |
| 360 | 54.0 |
| 720 | 63.0 |
Calculate the rate constant.
Following data are obtained for reaction :
N2O5 → 2NO2 + 1/2O2
| t/s | 0 | 300 | 600 |
| [N2O5]/mol L–1 | 1.6 × 10-2 | 0.8 × 10–2 | 0.4 × 10–2 |
1) Show that it follows first order reaction.
2) Calculate the half-life.
(Given log 2 = 0.3010, log 4 = 0.6021)
A first order reaction is 50% completed in 1.26 × 1014 s. How much time would it take for 100% completion?
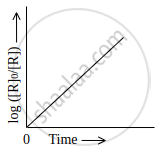
Which of the following graphs is correct for a first order reaction?

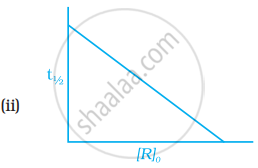
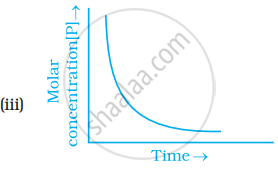
State a condition under which a bimolecular reaction is kinetically first order reaction.
With the help of an example explain what is meant by pseudo first order reaction.
The rate constant of a first order reaction is 6.9 × 10–3s–1. How much time will it take to reduce the initial concentration to its 1/8th value?
First order reaction is 50% complete in 1.26 × 1014s. How much time could it take for 100% completion?
Time required to decompose SO2Cl2 to half of its initial concentration is 60 minutes. If the de-composite is a first order reaction, calculated the rate constant of the reaction-
In a first order reaction the concentration of reactants decreases from 400mol L-1 to 25 mol L-1 in 200 seconds. The rate constant for the reaction is ______.
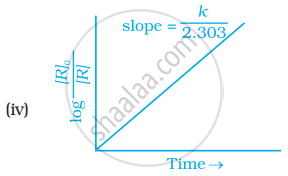
Observe the graph shown in figure and answer the following questions:
- What is the order of the reaction?
- What is the slope of the curve?
- Write the relationship between k and t1/2 (half life period).
Gaseous cyclobutene isomerizes to butadiene in a first order process which has a 'k' value of 3.3 × 10−4 s−1 at 153°C. The time in minutes it takes for the isomerization to proceed 40% to completion at this temperature is ______. (Rounded-off to the nearest integer)
For a first order reaction, the ratio of the time for 75% completion of a reaction to the time for 50% completion is ______. (Integer answer)
The slope in the plot of ln[R] vs. time for a first order reaction is ______.
The slope in the plot of `log ["R"]_0/(["R"])` Vs. time for a first-order reaction is ______.
Radioactive decay follows first-order kinetics. The initial amount of two radioactive elements X and Y is 1 gm each. What will be the ratio of X and Y after two days if their half-lives are 12 hours and 16 hours respectively?
How will you represent first order reactions graphically?
What is the rate constant?
Define first-order reaction.
The following data were obtained during the decomposition of SO2Cl2 at the constant volume. SO2Cl2 →SO2(g) + Cl2(g)
| Time (s) | Total Pressure (bar) |
| 0 | 0.5 |
| 100 | 0.6 |
Calculate the rate constant of the reaction.
Slove: \[\ce{2NOBr -> 2NO_{2(g)} + Br_{2(g)}}\]
For the above reaction, the rate law is rate = k[NOBr]2. If the rate of reaction is 6.5 × 10−6 mol L−1 s−1 at 2 × 10−3 mol L−1 concentration of NOBr, calculate the rate constant k for the reaction.
The rate constant for the reaction:
\[\ce{2N2O_{(s)} ->2N2O4_{(g)}}\] is 4.98 × 10-4 s-1.
The order of the reaction is ______.
Write the unit of rate constant [k] for the first order reaction.
