Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following problem.
A marble of mass 2m travelling at 6 cm/s is directly followed by another marble of mass m with double speed. After a collision, the heavier one travels with the average initial speed of the two. Calculate the coefficient of restitution.
उत्तर
Given: m1 = 2m, m2 = m, u1 = 6 cm/s,
u2 = 2u1 = 12 cm/s,
v1 = `("u"_1 + "u"_2)/2 = 9` cm/s
To find: Coefficient of restitution (e)
Formulae:
i. m1u1 + m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v2
ii. e = `("v"_2 - "v"_1)/("u"_1 - "u"_2)`
Calculation:
From formula (i),
[(2m) × 6] + (m × 12) = (2m × 9) + mv2
∴ 12 + 12 = 18 + v2
∴ v2 = 6 cm/s
From formula (ii),
e = `(6 - 9)/(6 - 12) = (- 3)/(-6) = 0.5`
The coefficient of restitution is 0.5.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State if the following statement is true or false. Give a reason for your answer.
In an inelastic collision, the final kinetic energy is always less than the initial kinetic energy of the system.
Answer carefully, with reason:
In an elastic collision of two billiard balls, is the total kinetic energy conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e. when they are in contact)?
Answer carefully, with reason:
Is the total linear momentum conserved during the short time of an elastic collision of two balls?
Answer carefully, with reason:
If the potential energy of two billiard balls depends only on the separation distance between their centres, is the collision elastic or inelastic? (Note, we are talking here of potential energy corresponding to the force during collision, not gravitational potential energy.)
The bob A of a pendulum released from 30° to the vertical hits another bob B of the same mass at rest on a table, as shown in the figure. How high does the bob A rise after the collision? Neglect the size of the bobs and assume the collision to be elastic.

A bullet of mass 0.012 kg and horizontal speed 70 m s–1 strikes a block of wood of mass 0.4 kg and instantly comes to rest with respect to the block. The block is suspended from the ceiling by means of thin wires. Calculate the height to which the block rises. Also, estimate the amount of heat produced in the block.
Which of the following potential energy curves in Fig. cannot possibly describe the elastic collision of two billiard balls? Here r is distance between centres of the balls.

Answer the following question.
A bullet of mass m1 travelling with a velocity u strikes a stationary wooden block of mass m2 and gets embedded into it. Determine the expression for loss in the kinetic energy of the system. Is this violating the principle of conservation of energy? If not, how can you account for this loss?
Explain the characteristics of elastic and inelastic collision.
Arrive at an expression for elastic collision in one dimension and discuss various cases.
In inelastic collision, ____________.
A mass M moving with velocity 'v' along x-axis collides and sticks to another mass 2M which is moving along Y-axis with velocity 3v. After collision, the velocity of the combination is ______.
A wooden block of mass 'M' moves with velocity 'v ' and collides with another block of mass '4M' which is at rest. After collision, the block of mass 'M' comes to rest. The coefficient of restitution will be ______.
A block of mass 'm' moving along a straight line with constant velocity `3vec"v"` collides with another block of same mass at rest. They stick together and move with common velocity. The common velocity is ______.
A bullet fired from gun with a velocity 30 m/s at an angle of 60° with horizontal direction. At the highest point of its path, the bullet explodes into two parts with masses in the ratio 1:3. The lighter mass comes to rest immediately. Then the speed of the heavier mass is
During inelastic collision between two bodies, which of the following quantities always remain conserved?
Consider a one-dimensional motion of a particle with total energy E. There are four regions A, B, C and D in which the relation between potential energy V, kinetic energy (K) and total energy E is as given below:
Region A : V > E
Region B : V < E
Region C : K > E
Region D : V > K
State with reason in each case whether a particle can be found in the given region or not.
The bob A of a pendulum released from horizontal to the vertical hits another bob B of the same mass at rest on a table as shown in figure.
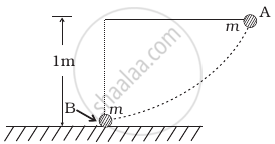
If the length of the pendulum is 1 m, calculate
- the height to which bob A will rise after collision.
- the speed with which bob B starts moving. Neglect the size of the bobs and assume the collision to be elastic.
Two pendulums with identical bobs and lengths are suspended from a common support such that in rest position the two bobs are in contact (Figure). One of the bobs is released after being displaced by 10° so that it collides elastically head-on with the other bob.

- Describe the motion of two bobs.
- Draw a graph showing variation in energy of either pendulum with time, for 0 ≤ t ≤ 2T, where T is the period of each pendulum.
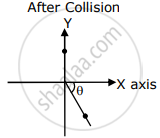
A ball of mass 10 kg moving with a velocity of 10`sqrt3` ms–1 along the X-axis, hits another ball of mass 20 kg which is at rest. After collision, the first ball comes to rest and the second one disintegrates into two equal pieces. One of the pieces starts moving along Y-axis at a speed of 10 m/s. The second piece starts moving at a speed of 20 m/s at an angle θ (degree) with respect to the X-axis.
The configuration of pieces after the collision is shown in the figure.
The value of θ to the nearest integer is ______.
A ball falls from a height of 1 m on a ground and it loses half its kinetic energy when it hits the ground. What would be the total distance covered by the ball after sufficiently long time?
A bag of sand of mass 9.8 kg is suspended by a rope. A bullet of 200 g travelling with speed 10 ms-1 gets embedded in it, then loss of kinetic energy will be ______.
An alpha-particle of mass m suffers 1-dimensional elastic collision with a nucleus at rest of unknown mass. It is scattered directly backwards losing, 64% of its initial kinetic energy. The mass of the nucleus is ______.
The dimension of mutual inductance is ______.
