Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following question using appropriate Euclid’s axiom:
Look at the figure. Show that length AH > sum of lengths of AB + BC + CD.

उत्तर
Given in the question, AB, BC and CD are parts of line.
Then, AB + BC + CD = AD ...(i)
And AD is the part of line AH.
Now, By Euclid’s axiom 5, the whole is greater than the part.
So, AH > AD
That is length AH > sum of length of AB + BC + CD ...[By using (i)]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give a definition of the following term. Are there other terms that need to be defined first? What are they, and how might you define them?
parallel lines
Give a definition of the following term. Are there other terms that need to be defined first? What are they, and how might you define them?
radius of a circle
How many least number of distinct points determine a unique line?
In how many points two distinct planes can intersect?
How many planes can be made to pass through a line and a point not on the line?
The number of interwoven isosceles triangles in Sriyantra (in the Atharvaveda) is ______.
Pythagoras was a student of ______.
“For every line l and for every point P not lying on a given line l, there exists a unique line m passing through P and parallel to l ” is known as Playfair’s axiom.
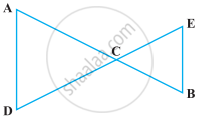
Solve the following question using appropriate Euclid’s axiom:
In the following figure, we have AC = DC, CB = CE. Show that AB = DE.
The following statement is true or false? Give reason for your answer.
There are an infinite number of lines which pass through two distinct points.
