Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State Gauss’Law.
उत्तर
Gauss’Law :
The electric flux `(phi_"E")` through any closed surface is equal to `1/in_0` times the 'net' change q enclosed by the surface.
`phi_"E" = oint vec"E" "d" vec"A" = "q"/in_0`
∈0 = Permittivity of free space.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
"For any charge configuration, equipotential surface through a point is normal to the electric field." Justify.
A point charge of 2.0 μC is at the centre of a cubic Gaussian surface 9.0 cm on edge. What is the net electric flux through the surface?
Electric intensity outside a charged cylinder having the charge per unit length 'λ' at a distance from its axis is ________.
(a) E = `(2pi in_0 lambda)/(Kr^2)`
(b) E = `(in_0 lambda)/(2piKr^2)`
(c) E = `lambda/(2piin_0Kr)`
(d) E = `(4piin_0lambda)/(Kr^2)`
A point charge q is at a distance of d/2 directly above the centre of a square of side d, as shown the figure. Use Gauss' law to obtain the expression for the electric flux through the square.
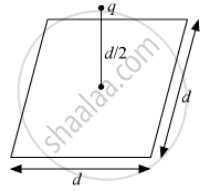
If the point charge is now moved to a distance 'd' from the centre of the square and the side of the square is doubled, explain how the electric flux will be affected.
Find the work done in bringing a charge q from perpendicular distance r1 to r2 (r2 > r1)
Two wires A and B of the same material and of equal length with the radii in the ratio 1 : 2 are subjected to identical loads. If the length of A increases by 8 mm, then the increase in length of B is:
A spherical ball contracts in volume by 0.02% when subjected to a pressure of 100 atmosphere. Assuming one atmosphere = 105 Nm−2, the bulk modulus of the material of the ball is:
Through two parallel wires A and B, 10A and 2A of currents are passed respectively in opposite directions. If the wire A is infinitely long and the length of the wire B is 2m, then force on the conductor B, which is situated at 10 cm distance from A, will be:
The electric field inside a spherical shell of uniform surface charge density is ______.
