Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Study the double bar graph given below and answer the questions that follow:

- What information is compared in the above given double bar graph?
- Calculate the ratio of minimum temperatures in the year 2008 to the year 2009 for the month of November.
- For how many months was the minimum temperature in the year 2008 greater than that of year 2009? Name those months.
- Find the average minimum temperature for the year 2008 for the four months.
- In which month is the variation in the two temperatures maximum?
उत्तर
a. The above double bar graph compares the minimum temperature during the month November to February for the years 2008 and 2009.
b. Minimum temperature of November in the year 2008 = 18°C
Minimum temperature of November in the year 2009 = 15°C
∴ Required ratio = 18/15 = 18:15 = 6:5
c. We can clearly see from the double bar graph that the minimum temperature in the year 2008 greater than that of the year 2009 for the month of February and November.
d. Average minimum temperature for the year 2008
= `"Total temperature for the year 2008 in four months"/4`
= `(18 + 11 + 4 + 12)/4`
= `45/4`
= 11.25
e. Difference of the temperature for different months can be shown by the following table:
| Month | Difference of temperature |
| November | 18 – 15 = 3 |
| December | 12 – 11 = 1 |
| January | 5 – 4 = 1 |
| Febuary | 12 – 8 = 4 |
From the above table, it is clear that for the month of February variation in two temperatures is maximum.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Number of children in six different classes are given below. Represent the data on a bar graph.
| Class | Fifth | Sixth | Seventh | Eighth | Ninth | Tenth |
| Number of children | 135 | 120 | 95 | 100 | 90 | 80 |
- How would you choose a scale?
- Answer the following questions:
- Which class has the maximum number of children? And the minimum?
- Find the ratio of students of class sixth to the students of class eight.
In a bar graph, each bar (rectangle) represents only one value of the numerical data.
In a bar graph, ______ can be drawn horizontally or vertically.
The bar graph given below represents the circulation of newspapers in different languages in a town. Study the bar graph and answer the following questions:
Scale: 1 unit length = 200 Newspapers
(a) What is the circulation of English newspaper?
(b) Name the two languages in which circulation of newspaper is the same.
(c) By how much is the circulation of newspaper in Hindi more than the newspaper in Bengali?
Read the bar graph given below and answer the following questions:
Scale: 1 unit = 50 students
(a) What information is given by the bar graph?
(b) In which year is the number of students maximum?
(c) In which year is the number of students twice as that of 2001 – 02?
(d) In which year did the number of students decrease as compared to previous year?
(e) In which year is the increase in number of students maximum as compared to the previous year?
Scale: 1 unit length = 200 km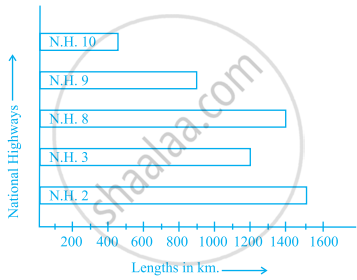
Prepare a pictograph of the data by taking a suitable symbol to represent 200 kilometers.
The bar graph given below represents the circulation of newspapers (dailies) in a town in six languages (the figures are approximated to hundreds).

Study the bar graph and answer the following questions:
- Find the total number of newspapers read in Hindi, Punjabi, Urdu, Marathi and Tamil.
- Find the excess number of newspapers read in Hindi than those in English.
- Name the language in which the least number of newspapers are read.
- Write the total circulation of newspapers in the town.
Observe the given data:
| Days of the week |
Mon | Tues | Wed | Thurs | Fri | Sat |
| Number of Mobile Phone Sets Sold |
50 | 45 | 30 | 55 | 27 | 60 |
- Draw a bar graph to represent the above given information.
- On which day of the week was the sales maximum?
- Find the total sales during the week.
- Find the ratio of the minimum sale to the maximum sale.
- Calculate the average sale during the week.
- On how many days of the week was the sale above the average sales?
Below is a list of 10 tallest buildings in India.
This list ranks buildings in India that stand at least 150 m (492 ft.) tall, based on standard height measurement. This includes spires and architectural details but does not include antenna marks. Following data is given as per the available information till 2009. Since new buildings are always under construction, go on-line to check new taller buildings.
Use the information given in the table about sky scrapers to answer the following questions:
| Name | City | Height | Floors | Year |
| Planet | Mumbai | 181 m | 51 | 2009 |
| UB Tower | Bengaluru | 184 m | 20 | 2006 |
| Ashok Towers | Mumbai | 193 m | 49 | 2009 |
| The Imperial I | Mumbai | 249 m | 60 | 2009 |
| The Imperial II | Mumbai | 249 m | 60 | 2009 |
| RNA Mirage | Mumbai | 180 m | 40 | 2009 |
| Oberoi Woods Tower I | Mumbai | 170 m | 40 | 2009 |
| Oberoi Woods Tower II | Mumbai | 170 m | 40 | 2009 |
| Oberoi Woods Tower III | Mumbai | 170 m | 40 | 2009 |
| MVRDC | Mumbai | 156 m | 35 | 2002 |
(a) Find the height of each storey of the three tallest buildings and write them in the following table:
| Building | Height | Number of storeys | Height of each storey |
(b) The average height of one storey for the buildings given in (a) is ______.
(c) Which city in this list has the largest percentage of skyscrapers? What is the percentage?
(d) What is the range of data?
(e) Find the median of the data.
(f) Draw a bar graph for given data.
The table below gives the data of tourists visiting 5 hill stations over two consecutive years. Study the table and answer the questions that follow:
| Hill stations | Nainital | Shimla | Manali | Mussoorie | Kullu |
| 2008 | 4000 | 5200 | 3700 | 5800 | 3500 |
| 2009 | 4800 | 4500 | 4200 | 6200 | 4600 |
- Draw a double bar graph to depict the above information using appropriate scale.
- Which hill station was visited by the maximum number of tourists in 2008?
- Which hill station was visited by the least number of tourists in 2009?
- In which hill stations was there increase in number of tourists in the year 2009?
