Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suggest reasons why the B–F bond lengths in BF3 (130 pm) and `"BF"_4^(-)` (143 pm) differ.
उत्तर
The B–F bond length in BF3 is shorter than the B–F bond length `"BF"_4^(-)`. BF3 is an electron-deficient species. With a vacant p-orbital on boron, the fluorine and boron atoms undergo pπ – pπ back-bonding to remove this deficiency. This imparts a double-bond character to the B–F bond.
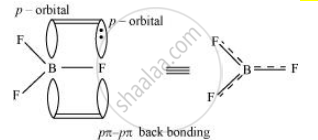
This double-bond character causes the bond length to shorten in BF3 (130 pm). However, when BF3 coordinates with the fluoride ion, a change in hybridisation from sp2 (in BF3) to sp3 (in `"BF"_4^(-)` ) occurs. Boron now forms 4σ bonds and the double-bond character is lost. This accounts for a B–F bond length of 143 pm in `"BF"_4^(-)` ion.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the structure of diborane ______.
Dry ice is ______.
Cement, the important building material is a mixture of oxides of several elements. Besides calcium, iron and sulphur, oxides of elements of which of the group (s) are present in the mixture?
Which of the following statements are correct. Answer on the basis of Figure.

(i) The two birdged hydrogen atoms and the two boron atoms lie in one plane;
(ii) Out of six B – H bonds two bonds can be described in terms of 3 centre 2-electron bonds.
(iii) Out of six B – H bonds four B – H bonds can be described in terms of 3 centre 2 electron bonds;
(iv) The four-terminal B – H bonds are two centre-two electron regular bonds.
Explain why the following compounds behave as Lewis acids?
AlCl3
Aluminium dissolves in mineral acids and aqueous alkalies and thus shows amphoteric character. A piece of aluminium foil is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sodium hydroxide solution in a test tube and on bringing a burning matchstick near the mouth of the test tube, a pop sound indicates the evolution of hydrogen gas. The same activity when performed with concentrated nitric acid, reaction doesn’t proceed. Explain the reason.
Identify the compounds A, X and Z in the following reactions:
\[\ce{X ->[Δ][370 K] HBO2 ->[Δ][> 370 K] Z}\]
Describe the general trends in the following properties of the elements in Groups 13 and 14.
Atomic size
Describe the general trends in the following properties of the elements in Groups 13 and 14.
Ionisation enthalpy
Describe the general trends in the following properties of the elements in Groups 13 and 14.
Nature of halides
Account for the following observations:
Though fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine yet BF3 is a weaker Lewis acid than BCl3
Account for the following observations:
PbO2 is a stronger oxidising agent than SnO2
Account for the following observations:
The +1 oxidation state of thallium is more stable than its +3 state.
Three pairs of compounds are given below. Identify that compound in each of the pairs which has group 13 element in more stable oxidation state. Give reason for your choice. State the nature of bonding also.
AlCl3 , AlCl
BCl3 exists as monomer whereas AlCl3 is dimerised through halogen bridging. Give reason. Explain the structure of the dimer of AlCl3 also.
Boron compounds behave as Lewis acids because of their ______.
Which one of the following is the correct statement?
