Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The pressure-volume work for an ideal gas can be calculated by using the expression w = `- int_(v_i)^(v_f) p_(ex) dV`. The work can also be calculated from the pV– plot by using the area under the curve within the specified limits. When an ideal gas is compressed (a) reversibly or (b) irreversibly from volume Vi to Vf. choose the correct option.
पर्याय
w (reversible) = w (irreversible)
w (reversible) < w (irreversible)
w (reversible) > w (irreversible)
w (reversible) = w (irreversible) + `P_(ex).∆V`
उत्तर
w (reversible) < w (irreversible)
Explanation:
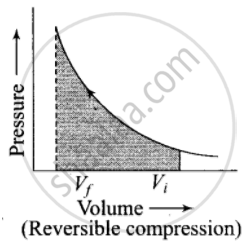
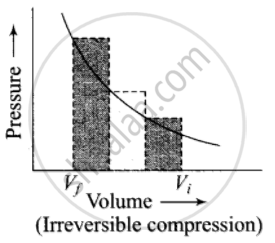
Area under the curve is greater in irreversible compression than that of reversible compression.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A sample of 1.0 mol of a monoatomic ideal gas is taken through a cyclic process of expansion and compression as shown in figure 6.1. What will be the value of ∆H for the cycle as a whole?

Expansion of a gas in vacuum is called free expansion. Calculate the work done and the change in internal energy when 1 litre of ideal gas expands isothermally into vacuum until its total volume is 5 litre?
Represent the potential energy/enthalpy change in the following processes graphically.
(a) Throwing a stone from the ground to roof.
(b) \[\ce{1/2 H2(g) + 1/2 Cl2 (g) ⇌ HCl (g) Δ_rH^Θ = - 92.32 kJ mol^{-1}}\]
In which of the processes potential energy/enthalpy change is contributing factor to the spontaneity?
An ideal gas is allowed to expand against a constant pressure of 2 bar from 10 L to 50 L in one step. Calculate the amount of work done by the gas. If the same expansion were carried out reversibly, will the work done be higher or lower than the earlier case? (Given that 1 L bar = 100 J)
Graphically show the total work done in an expansion when the state of an ideal gas is changed reversibly and isothermally from \[\ce{(p_i, V_i)}\] to \[\ce{(p_f , V_f )}\]. With the help of a pV plot compare the work done in the above case with that carried out against a constant external pressure \[\ce{p_f}\].
For silver Cp (J K-1 mol-1) = 23 + 0.01 T. If the temperature (T) of 3 moles of silver is raised from 300 K to 1000 K at 1 atom pressure, the value of ΔH will be close to ______.
Calculate the work involved when 1 mol of an ideal gas is compressed reversibly from 1.00 bar to 5.00 bar at a constant temperature of 300 K ______.
1 mole of an ideal monoatomic gas initially at 1 atm and 300 K experiences a process by which pressure is doubled. The nature of the process is unspecified but 6. ΔU = 900 cal. The final volume will be ______ l.
[Given : R = 0.08 atm lit. I mol/K = 2 Cal/K/mol J]
Five moles of an ideal gas at 1 bar and 298 K is expanded into the vacuum to double the volume. The work done is ______.
An ideal gas expands in volume from 1 × 10−3 to 1 × 10−2 m3 at 300 K against a constant pressure of 1 × 105 Nm−2. The work done is ______.
