Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The variation of angular position θ, of a point on a rotating rigid body, with time t is shown in figure. Is the body rotating clock-wise or anti-clockwise?
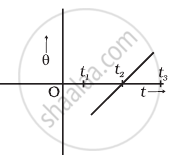
उत्तर
As the slope of θ-t graph is positive and a positive slope indicates anti-clockwise rotation which is traditionally taken as positive.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A sphere rolls on a horizontal surface. If there any point of the sphere which has a vertical velocity?
A body is in pure rotation. The linear speed \[\nu\] of a particle, the distance r of the particle from the axis and the angular velocity \[\omega\] of the body are related as \[\omega = \frac{\nu}{r}.\] Thus
A sphere is rolled on a rough horizontal surface. If gradually slows down and stops. The force of friction tries to
(a) decrease the linear velocity
(b) increase the angular velocity
(c) increase the linear momentum
(d) decrease the angular velocity.
Find the angular velocity of a body rotating with an acceleration of 2 rev/s2 as it completes the 5th revolution after the start.
A disc of radius 10 cm is rotating about its axis at an angular speed of 20 rad/s. Find the linear speed of the middle point of a radius.
A cylinder rotating at an angular speed of 50 rev/s is brought in contact with an identical stationary cylinder. Because of the kinetic friction, torques act on the two cylinders accelerating the stationary one and decelerating the moving one. If the common magnitude of the acceleration and deceleration be one revolution per second square, how long will it take before the two cylinders have equal angular speed?
A dumb-bell consists of two identical small balls of mass 1/2 kg each connected to the two ends of a 50 cm long light rod. The dumb-bell is rotating about a fixed axis thorough the centre of the rod and perpendicular to it at an angular speed of 10 rad/s. An impulsive force of average magnitude 5⋅0 N acts on one of the masses in the direction of its velocity for 0⋅10 s. Find the new angular velocity of the system.
Suppose the platform of the previous problem is brought to rest with the ball in the hand of the kid standing on the rim. The kid throws the ball horizontally to his friend in a direction tangential to the rim with a speed \[\nu\] as seen by his friend. Find the angular velocity with which the platform will start rotating.
A ball falls on the ground from a height of 2.0 m and rebounds up to a height of 1.5 m. Find the coefficient of restitution.
Two cylindrical hollow drums of radii R and 2R, and of a common height h, are rotating with angular velocities ω(anti-clockwise) and ω(clockwise), respectively. Their axes, fixed are parallel and in a horizontal plane separated by (3R + δ). They are now brought in contact (δ → 0).
- Show the frictional forces just after contact.
- Identify forces and torques external to the system just after contact.
- What would be the ratio of final angular velocities when friction ceases?
