Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why does a solid sphere have smaller moment of inertia than a hollow cylinder of same mass and radius, about an axis passing through their axes of symmetry?
उत्तर
Moment of inertia of a particle l = mr2 where r is the perpendicular distance of particle from the rotational axis.
The moment of inertia of a body made up of a number of particles (discrete distribution)
I = m1r12 + m2r22 + m3r32
Moment of inertia of a continuous distribution of mass, treating the element of mass dm at position r as particle
dl = dmr2
MI is not constant for a body. It depends on the axis of rotation.
MI depends on the mass of the body. The higher the mass, the higher the MI.
MI depends on the distribution of the mass about an axis. The farther the mass is distributed from the axis, the higher will be the MI.
Moment of inertia depends on mass, distribution of mass and on the position of axis of rotation.
All the mass in a cylinder lies at a distance R from the axis of symmetry but most of the mass of a solid sphere lies at a smaller distance than R.
Therefore, `I_"hollwcylinder" > I_"sphere"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Find the moment of inertia of a sphere about a tangent to the sphere, given the moment of inertia of the sphere about any of its diameters to be 2MR2/5, where M is the mass of the sphere and R is the radius of the sphere.
Torques of equal magnitude are applied to a hollow cylinder and a solid sphere, both having the same mass and radius. The cylinder is free to rotate about its standard axis of symmetry, and the sphere is free to rotate about an axis passing through its centre. Which of the two will acquire a greater angular speed after a given time?
Show that the child’s new kinetic energy of rotation is more than the initial kinetic energy of rotation. How do you account for this increase in kinetic energy?
A hoop of radius 2 m weighs 100 kg. It rolls along a horizontal floor so that its centre of mass has a speed of 20 cm/s. How much work has to be done to stop it?
A solid cylinder rolls up an inclined plane of angle of inclination 30°. At the bottom of the inclined plane, the centre of mass of the cylinder has a speed of 5 m/s.
(a) How far will the cylinder go up the plane?
(b) How long will it take to return to the bottom?
A bullet of mass 10 g and speed 500 m/s is fired into a door and gets embedded exactly at the centre of the door. The door is 1.0 m wide and weighs 12 kg. It is hinged at one end and rotates about a vertical axis practically without friction. Find the angular speed of the door just after the bullet embeds into it.
(Hint: The moment of inertia of the door about the vertical axis at one end is ML2/3.)
The pulley shown in the following figure has a radius 10 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅5 kg-m2about its axis. Assuming the inclined planes to be frictionless, calculate the acceleration of the 4⋅0 kg block.
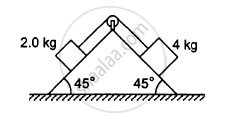
Solve the previous problem if the friction coefficient between the 2⋅0 kg block and the plane below it is 0⋅5 and the plane below the 4⋅0 kg block is frictionless.
A uniform metre stick of mass 200 g is suspended from the ceiling thorough two vertical strings of equal lengths fixed at the ends. A small object of mass 20 g is placed on the stick at a distance of 70 cm from the left end. Find the tensions in the two strings.
A thin circular plate of mass M and radius R has its density varying as ρ(r) = ρ0r with ρ0 as constant and r is the distance from its center. The moment of Inertia of the circular plate about an axis perpendicular to the plate and passing through its edge is I = a MR2. The value of the coefficient a is ______.
