Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
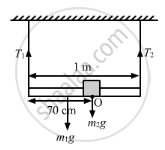
A uniform metre stick of mass 200 g is suspended from the ceiling thorough two vertical strings of equal lengths fixed at the ends. A small object of mass 20 g is placed on the stick at a distance of 70 cm from the left end. Find the tensions in the two strings.
उत्तर
Given
Mass of the stick
\[m_1 = 200 g\]
Mass of the small object = \[m_2 = 20\]
Length of the string = \[l = 1 m\]
As the system is in equilibrium, we have
\[\tau_{\text{total}} = 0 \left(\text{about O}\right)\]
\[\left( T_1 \times r_1 \right) - \left( T_2 \times r_2 \right) - \left( m_1 g \times r_3 \right) = 0\]
\[\Rightarrow T_1 \times 0 . 7 - T_2 \times 0 . 3 - 2 \times 0 . 2 \times g = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow 7 T_1 - 3 T_2 = 3 . 92 ...........(1)\]
Now, we have
Total upward force = Total downward force
\[T_1 + T_2 = m_1 g + m_2 g\]
\[= 0 . 2 \times 9 . 8 + 0 . 02 \times 9 . 8\]
\[ \Rightarrow T_1 + T_2 = 2 . 156 ..........(2)\]
Solving equations (1) and (2), we get
\[T_1 = 1 . 038 N \approx 1 . 04 N; \]
\[ T_2 = 1 . 18 \approx 1 . 12 N\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A child stands at the centre of a turntable with his two arms outstretched. The turntable is set rotating with an angular speed of 40 rev/min. How much is the angular speed of the child if he folds his hands back and thereby reduces his moment of inertia to 2/5 times the initial value? Assume that the turntable rotates without friction.
Show that the child’s new kinetic energy of rotation is more than the initial kinetic energy of rotation. How do you account for this increase in kinetic energy?
A hoop of radius 2 m weighs 100 kg. It rolls along a horizontal floor so that its centre of mass has a speed of 20 cm/s. How much work has to be done to stop it?
The oxygen molecule has a mass of 5.30 × 10–26 kg and a moment of inertia of 1.94×10–46 kg m2 about an axis through its centre perpendicular to the lines joining the two atoms. Suppose the mean speed of such a molecule in a gas is 500 m/s and that its kinetic energy of rotation is two thirds of its kinetic energy of translation. Find the average angular velocity of the molecule.
A bullet of mass 10 g and speed 500 m/s is fired into a door and gets embedded exactly at the centre of the door. The door is 1.0 m wide and weighs 12 kg. It is hinged at one end and rotates about a vertical axis practically without friction. Find the angular speed of the door just after the bullet embeds into it.
(Hint: The moment of inertia of the door about the vertical axis at one end is ML2/3.)
A cylinder of mass 10 kg and radius 15 cm is rolling perfectly on a plane of inclination 30°. The coefficient of static friction µs = 0.25.
(a) How much is the force of friction acting on the cylinder?
(b) What is the work done against friction during rolling?
(c) If the inclination θ of the plane is increased, at what value of θ does the cylinder begin to skid, and not roll perfectly?
Let I1 an I2 be the moments of inertia of two bodies of identical geometrical shape, the first made of aluminium and the second of iron.
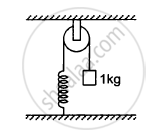
A string is wrapped on a wheel of moment of inertia 0⋅20 kg-m2 and radius 10 cm and goes through a light pulley to support a block of mass 2⋅0 kg as shown in the following figure. Find the acceleration of the block.
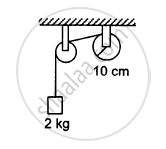
Suppose the smaller pulley of the previous problem has its radius 5⋅0 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅10 kg-m2. Find the tension in the part of the string joining the pulleys.
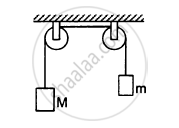
The pulleys shown in the following figure are identical, each having a radius R and moment of inertia I. Find the acceleration of the block M.
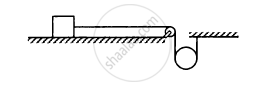
The descending pulley shown in the following figure has a radius 20 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅20 kg-m2. The fixed pulley is light and the horizontal plane frictionless. Find the acceleration of the block if its mass is 1⋅0 kg.
A boy is seated in a revolving chair revolving at an angular speed of 120 revolutions per minute. Two heavy balls form part of the revolving system and the boy can pull the balls closer to himself or may push them apart. If by pulling the balls closer, the boy decreases the moment of inertia of the system from 6 kg-m2 to 2 kg-m2, what will be the new angular speed?
The pulley shown in the following figure has a radius of 20 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅2 kg-m2. The string going over it is attached at one end to a vertical spring of spring constant 50 N/m fixed from below, and supports a 1 kg mass at the other end. The system is released from rest with the spring at its natural length. Find the speed of the block when it has descended through 10 cm. Take g = 10 m/s2.
From a circular ring of mass, ‘M’ and radius ‘R’ an arc corresponding to a 90° sector is removed. The moment of inertia of the remaining part of the ring about an axis passing through the centre of the ring and perpendicular to the plane of the ring is ‘K’ times ‘MR2’. Then the value of ‘K’ is ______.
From a circular ring of mass ‘M’ and radius ‘R’ an arc corresponding to a 90° sector is removed. The moment of inertia of the remaining part of the ring about an axis passing through the centre of the ring and perpendicular to the plane of the ring is ‘K’ times ‘MR2 ’. Then the value of ‘K’ is ______.
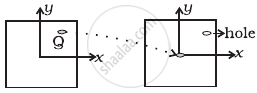
A uniform square plate has a small piece Q of an irregular shape removed and glued to the centre of the plate leaving a hole behind (Figure). The moment of inertia about the z-axis is then ______.
Consider a badminton racket with length scales as shown in the figure.
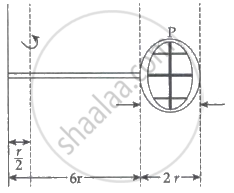
If the mass of the linear and circular portions of the badminton racket is the same (M) and the mass of the threads is negligible, the moment of inertia of the racket about an axis perpendicular to the handle and in the plane of the ring at, `r/2` distance from the ends A of the handle will be ______ Mr2.
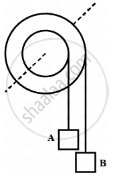
The figure shows a small wheel fixed coaxially on a bigger one of double the radius. The system rotates about the common axis. The strings supporting A and B do not slip on the wheels. If x and y be the distances travelled by A and B in the same time interval, then ______.
A cubical block of mass 6 kg and side 16.1 cm is placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. It is hit by a cue at the top to impart impulse in the horizontal direction. The minimum impulse imparted to topple the block must be greater than ______ kg m/s.
