Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A boy is seated in a revolving chair revolving at an angular speed of 120 revolutions per minute. Two heavy balls form part of the revolving system and the boy can pull the balls closer to himself or may push them apart. If by pulling the balls closer, the boy decreases the moment of inertia of the system from 6 kg-m2 to 2 kg-m2, what will be the new angular speed?
उत्तर
Given
Initial angular speed of the system,
\[\omega_1 = 120\text{ rpm }= 120 \times \left( \frac{2\pi}{60} \right) = 4\pi\text{ rad/s}\]
Initial moment of inertia of the system,
\[I_1 = 6 kg - m^2\]
Final moment of inertia of the system,
\[I_2 = 2 kg - m^2\]
Two balls are inside the system; therefore, we get
Total external torque = 0
\[I_2 = 2 kg - m^2\]
\[\therefore I_1 \omega_1 = I_2 \omega_2\]
\[\Rightarrow 6 \times 4\pi = 2 \omega_2 \]
\[ \Rightarrow \omega_2 = 12\pi rad/s\]
\[\text{Or, }\omega_2 = 6\text{ rev/s }= 360\text{ rev/minute}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Show that the child’s new kinetic energy of rotation is more than the initial kinetic energy of rotation. How do you account for this increase in kinetic energy?
A rope of negligible mass is wound round a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N? What is the linear acceleration of the rope? Assume that there is no slipping.
A solid cylinder rolls up an inclined plane of angle of inclination 30°. At the bottom of the inclined plane, the centre of mass of the cylinder has a speed of 5 m/s.
(a) How far will the cylinder go up the plane?
(b) How long will it take to return to the bottom?
A bullet of mass 10 g and speed 500 m/s is fired into a door and gets embedded exactly at the centre of the door. The door is 1.0 m wide and weighs 12 kg. It is hinged at one end and rotates about a vertical axis practically without friction. Find the angular speed of the door just after the bullet embeds into it.
(Hint: The moment of inertia of the door about the vertical axis at one end is ML2/3.)
A body having its centre of mass at the origin has three of its particles at (a,0,0), (0,a,0), (0,0,a). The moments of inertia of the body about the X and Y axes are 0⋅20 kg-m2 each. The moment of inertia about the Z-axis
Let IA and IB be moments of inertia of a body about two axes A and B respectively. The axis A passes through the centre of mass of the body but B does not.
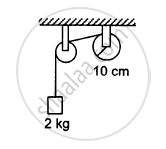
A string is wrapped on a wheel of moment of inertia 0⋅20 kg-m2 and radius 10 cm and goes through a light pulley to support a block of mass 2⋅0 kg as shown in the following figure. Find the acceleration of the block.
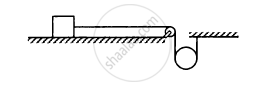
The descending pulley shown in the following figure has a radius 20 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅20 kg-m2. The fixed pulley is light and the horizontal plane frictionless. Find the acceleration of the block if its mass is 1⋅0 kg.
Solve the previous problem if the friction coefficient between the 2⋅0 kg block and the plane below it is 0⋅5 and the plane below the 4⋅0 kg block is frictionless.
A uniform metre stick of mass 200 g is suspended from the ceiling thorough two vertical strings of equal lengths fixed at the ends. A small object of mass 20 g is placed on the stick at a distance of 70 cm from the left end. Find the tensions in the two strings.
A wheel of moment of inertia 0⋅500 kg-m2 and radius 20⋅0 cm is rotating about its axis at an angular speed of 20⋅0 rad/s. It picks up a stationary particle of mass 200 g at its edge. Find the new angular speed of the wheel.
A diver having a moment of inertia of 6⋅0 kg-m2 about an axis thorough its centre of mass rotates at an angular speed of 2 rad/s about this axis. If he folds his hands and feet to decrease the moment of inertia to 5⋅0 kg-m2, what will be the new angular speed?
A wheel of moment of inertia 0⋅10 kg-m2 is rotating about a shaft at an angular speed of 160 rev/minute. A second wheel is set into rotation at 300 rev/minute and is coupled to the same shaft so that both the wheels finally rotate with a common angular speed of 200 rev/minute. Find the moment of inertia of the second wheel.
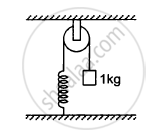
The pulley shown in the following figure has a radius of 20 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅2 kg-m2. The string going over it is attached at one end to a vertical spring of spring constant 50 N/m fixed from below, and supports a 1 kg mass at the other end. The system is released from rest with the spring at its natural length. Find the speed of the block when it has descended through 10 cm. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Four bodies of masses 2 kg, 3 kg, 4 kg and 5 kg are placed at points A, B, C, and D respectively of a square ABCD of side 1 metre. The radius of gyration of the system about an axis passing through A and perpendicular to plane is
A wheel of mass 15 kg has a moment of inertia of 200 kg-m2 about its own axis, the radius of gyration will be:
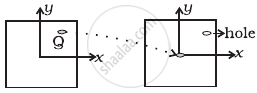
A uniform square plate has a small piece Q of an irregular shape removed and glued to the centre of the plate leaving a hole behind (Figure). The moment of inertia about the z-axis is then ______.