Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two monochromatic beams A and B of equal intensity I, hit a screen. The number of photons hitting the screen by beam A is twice that by beam B. Then what inference can you make about their frequencies?
उत्तर
Effect of intensity: If the intensity of light is increased (while its frequency is kept the same) the current levels off at a higher value, showing that more electrons are being emitted per unit of time. But the stopping potential V0 doesn't change, i.e. Intensity `∝` no . of incident photon no. of emitted photoelectron per time photocurrent.

Effect of frequency: If the frequency of incident light increases, (keeping intensity constant) stopping potential increases but there is no change in photoelectric current.
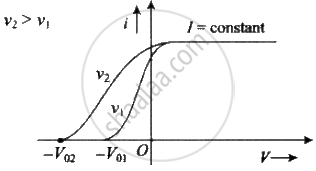
Let us assume nA is the number of photons falling per second of beam A and nB is the number of photons falling per second of beam B.
And it is given that the number of photons hitting the screen by beam A is twice that by beam B.nA = 2nB
The energy of the falling photon of beam A = hvA
The energy of a falling photon of beam B = hvB
Now, according to the question, the intensity of A is equal to the intensity of B.
Therefore, I = nAvA = nBvB
⇒ `v_A/v_B = n_B/n_A = n_B/(2n_B) = 1/2`
⇒ vB = 2vA
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Ultraviolet light of wavelength 2271 Å from a 100 W mercury source irradiates a photo-cell made of molybdenum metal. If the stopping potential is −1.3 V, estimate the work function of the metal. How would the photo-cell respond to a high intensity (∼105 W m−2) red light of wavelength 6328 Å produced by a He-Ne laser?
The work function for the following metals is given:
Na: 2.75 eV; K: 2.30 eV; Mo: 4.17 eV; Ni: 5.15 eV
Which of these metals will not give photoelectric emission for a radiation of wavelength 3300 Å from a He-Cd laser placed 1 m away from the photocell? What happens if the laser is brought nearer and placed 50 cm away?
The threshold wavelength of a metal is λ0. Light of wavelength slightly less than λ0 is incident on an insulated plate made of this metal. It is found that photoelectrons are emitted for some time and after that the emission stops. Explain.
A totally reflecting, small plane mirror placed horizontally faces a parallel beam of light, as shown in the figure. The mass of the mirror is 20 g. Assume that there is no absorption in the lens and that 30% of the light emitted by the source goes through the lens. Find the power of the source needed to support the weight of the mirror.
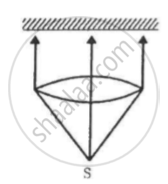
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Find the maximum magnitude of the linear momentum of a photoelectron emitted when a wavelength of 400 nm falls on a metal with work function 2.5 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Define the term: threshold frequency
In photoelectric effect, the photoelectric current started to flow. This means that the frequency of incident radiations is ______.
In photoelectric effect the photo current ______.
Consider a 20 W bulb emitting light of wavelength 5000 Å and shining on a metal surface kept at a distance 2 m. Assume that the metal surface has work function of 2 eV and that each atom on the metal surface can be treated as a circular disk of radius 1.5 Å.
- Estimate no. of photons emitted by the bulb per second. [Assume no other losses]
- Will there be photoelectric emission?
- How much time would be required by the atomic disk to receive energy equal to work function (2 eV)?
- How many photons would atomic disk receive within time duration calculated in (iii) above?
- Can you explain how photoelectric effect was observed instantaneously?
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
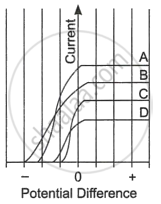
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
