Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A totally reflecting, small plane mirror placed horizontally faces a parallel beam of light, as shown in the figure. The mass of the mirror is 20 g. Assume that there is no absorption in the lens and that 30% of the light emitted by the source goes through the lens. Find the power of the source needed to support the weight of the mirror.
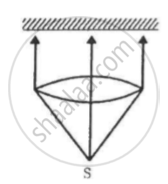
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
उत्तर
Given :-
Mass of the mirror, m = 20 g = 20 × 10−3 kg
The weight of the mirror will be balanced if the force exerted by the photons will be equal to the weight of the mirror.
Now,
Relation between wavelength `(λ)` and momentum (p) :-
`p = h/λ`
On divinding both sides by t , we get
`P/t = h/(λt)...............(1)`
Energy,
`E = (hc)/λ`
⇒ `E/t = (hc)/(λt)`
Let P be the power. Then,
`P = E/t = (hc)/(λt)`
`P = (pc)/t ............ ["Using equation (1)"]`
⇒ `P/c = p/t`
Force ,
`F = P/t = P/c ..............("Since F" = ("Momentum")/("Time"))`
Thus, rate of change of momentum = Power/c
As the light gets reflected normally,
Force exerted = 2 (Rate of change of momentum) = 2 × Power/c
`30% "of" ((2 xx "Power")/c) = "mg"`
`⇒ "Power" = (20 xx 10^-3 xx 10 xx 3 xx 10^8 xx 10)/(2 xx 3)= 100" MW"`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The photoelectric cut-off voltage in a certain experiment is 1.5 V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted?
The work function for the following metals is given:
Na: 2.75 eV; K: 2.30 eV; Mo: 4.17 eV; Ni: 5.15 eV
Which of these metals will not give photoelectric emission for a radiation of wavelength 3300 Å from a He-Cd laser placed 1 m away from the photocell? What happens if the laser is brought nearer and placed 50 cm away?
Light of intensity 10−5 W m−2 falls on a sodium photo-cell of surface area 2 cm2. Assuming that the top 5 layers of sodium absorb the incident energy, estimate time required for photoelectric emission in the wave-picture of radiation. The work function for the metal is given to be about 2 eV. What is the implication of your answer?
The following graph shows the variation of photocurrent for a photosensitive metal :
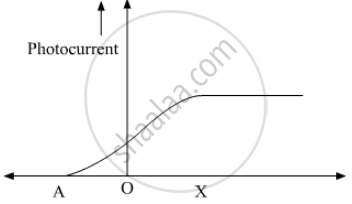
(a) Identify the variable X on the horizontal axis.
(b) What does the point A on the horizontal axis represent?
(c) Draw this graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation v1, v2 and v3 (v1 > v2 > v3) for same intensity.
(d) Draw this graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I1 > I2 > I3) having same frequency.
Can we find the mass of a photon by the definition p = mv?
The threshold wavelength of a metal is λ0. Light of wavelength slightly less than λ0 is incident on an insulated plate made of this metal. It is found that photoelectrons are emitted for some time and after that the emission stops. Explain.
Let nr and nb be the number of photons emitted by a red bulb and a blue bulb, respectively, of equal power in a given time.
A point source of light is used in a photoelectric effect. If the source is removed farther from the emitting metal, the stopping potential
If the wavelength of light in an experiment on photoelectric effect is doubled,
(a) photoelectric emission will not take place
(b) photoelectric emission may or may not take place
(c) the stopping potential will increase
(d) the stopping potential will decrease
The work function of a photoelectric material is 4.0 eV. (a) What is the threshold wavelength? (b) Find the wavelength of light for which the stopping potential is 2.5 V.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Find the maximum magnitude of the linear momentum of a photoelectron emitted when a wavelength of 400 nm falls on a metal with work function 2.5 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The electric field associated with a light wave is given by `E = E_0 sin [(1.57 xx 10^7 "m"^-1)(x - ct)]`. Find the stopping potential when this light is used in an experiment on photoelectric effect with the emitter having work function 1.9 eV.
In the case of photoelectric effect experiment, explain the following facts, giving reasons.
The photoelectric current increases with increase of intensity of incident light.
Define the term: stopping potential in the photoelectric effect.
Consider a thin target (10–2 cm square, 10–3 m thickness) of sodium, which produces a photocurrent of 100 µA when a light of intensity 100W/m2 (λ = 660 nm) falls on it. Find the probability that a photoelectron is produced when a photons strikes a sodium atom. [Take density of Na = 0.97 kg/m3].
How would the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface change if the intensity of incident radiation was decreased? Justify your answer.
A metallic plate exposed to white light emits electrons. For which of the following colours of light, the stopping potential will be maximum?
