Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The following graph shows the variation of photocurrent for a photosensitive metal :
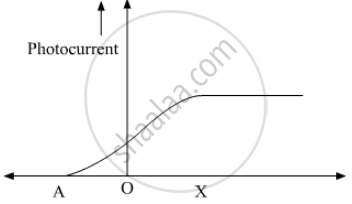
(a) Identify the variable X on the horizontal axis.
(b) What does the point A on the horizontal axis represent?
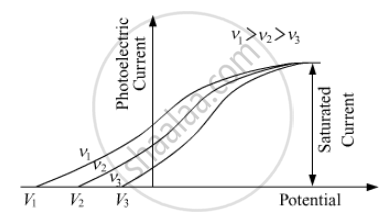
(c) Draw this graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation v1, v2 and v3 (v1 > v2 > v3) for same intensity.
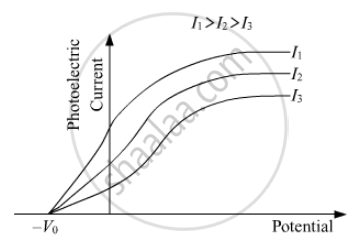
(d) Draw this graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I1 > I2 > I3) having same frequency.
उत्तर
(a) Variable X is the accelerating potential applied across the photosensitive material.
(b) A represents the stopping potential for the given photosensitive metal. Stopping potential is the minimum negative potential V0 applied across the photosensitive material at which the photoelectric current becomes zero.
(c) Graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation v1, v2 and v3 (v1 > v2 > v3) for same intensity
(d) Graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I1 > I2 > I3) having same frequency
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Can we find the mass of a photon by the definition p = mv?
The threshold wavelength of a metal is λ0. Light of wavelength slightly less than λ0 is incident on an insulated plate made of this metal. It is found that photoelectrons are emitted for some time and after that the emission stops. Explain.
Photoelectric effect supports quantum nature of light because
(a) there is a minimum frequency below which no photoelectrons are emitted
(b) the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons depends only on the frequency of light and not on its intensity
(c) even when the metal surface is faintly illuminated the photoelectrons leave the surface immediately
(d) electric charge of the photoelectrons is quantised
A beam of white light is incident normally on a plane surface absorbing 70% of the light and reflecting the rest. If the incident beam carries 10 W of power, find the force exerted by it on the surface.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The work function of a photoelectric material is 4.0 eV. (a) What is the threshold wavelength? (b) Find the wavelength of light for which the stopping potential is 2.5 V.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
In photoelectric effect the photo current ______.
Consider a thin target (10–2 cm square, 10–3 m thickness) of sodium, which produces a photocurrent of 100 µA when a light of intensity 100W/m2 (λ = 660 nm) falls on it. Find the probability that a photoelectron is produced when a photons strikes a sodium atom. [Take density of Na = 0.97 kg/m3].
Why it is the frequency and not the intensity of the light source that determines whether the emission of photoelectrons will occur or not? Explain.
How would the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface change if the frequency of the incident radiation were increased? Justify your answer.
What is the effect of threshold frequency and stopping potential on increasing the frequency of the incident beam of light? Justify your answer.
