Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The following graph shows the variation of photocurrent for a photosensitive metal :
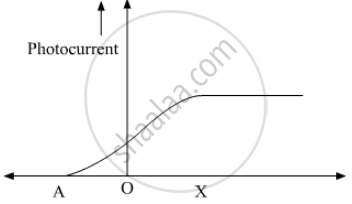
(a) Identify the variable X on the horizontal axis.
(b) What does the point A on the horizontal axis represent?
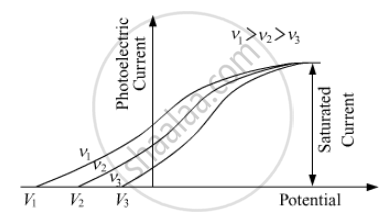
(c) Draw this graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation v1, v2 and v3 (v1 > v2 > v3) for same intensity.
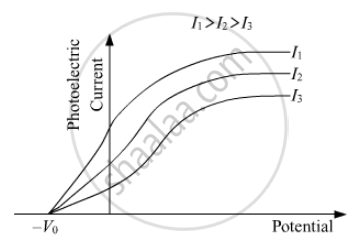
(d) Draw this graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I1 > I2 > I3) having same frequency.
Solution
(a) Variable X is the accelerating potential applied across the photosensitive material.
(b) A represents the stopping potential for the given photosensitive metal. Stopping potential is the minimum negative potential V0 applied across the photosensitive material at which the photoelectric current becomes zero.
(c) Graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation v1, v2 and v3 (v1 > v2 > v3) for same intensity
(d) Graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I1 > I2 > I3) having same frequency
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The photoelectric cut-off voltage in a certain experiment is 1.5 V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted?
The equation E = pc is valid
Light of wavelength λ falls on a metal with work-function hc/λ0. Photoelectric effect will take place only if
When stopping potential is applied in an experiment on photoelectric effect, no photoelectric is observed. This means that
When the intensity of a light source in increased,
(a) the number of photons emitted by the source in unit time increases
(b) the total energy of the photons emitted per unit time increases
(c) more energetic photons are emitted
(d) faster photons are emitted
In which of the following situations, the heavier of the two particles has smaller de Broglie wavelength? The two particles
(a) move with the same speed
(b) move with the same linear momentum
(c) move with the same kinetic energy
(d) have fallen through the same height
The work function of a photoelectric material is 4.0 eV. (a) What is the threshold wavelength? (b) Find the wavelength of light for which the stopping potential is 2.5 V.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Find the maximum magnitude of the linear momentum of a photoelectron emitted when a wavelength of 400 nm falls on a metal with work function 2.5 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Define the term: stopping potential in the photoelectric effect.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
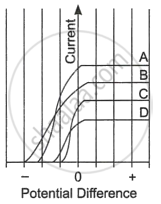
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
