Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The photoelectric cut-off voltage in a certain experiment is 1.5 V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted?
Solution
Photoelectric cut-off voltage, V0 = 1.5 V
The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons is given as:
`"K"_"e" = "eV"_0`
Where,
e = Charge on an electron = 1.6 × 10−19 C
∴ Ke = 1.6 × 10−19 × 1.5
= 2.4 × 10−19 J
Therefore, the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in the given experiment is 2.4 × 10−19 J.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Every metal has a definite work function. Why do all photoelectrons not come out with the same energy if incident radiation is monochromatic? Why is there an energy distribution of photoelectrons?
The following graph shows the variation of photocurrent for a photosensitive metal :
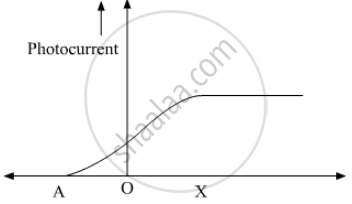
(a) Identify the variable X on the horizontal axis.
(b) What does the point A on the horizontal axis represent?
(c) Draw this graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation v1, v2 and v3 (v1 > v2 > v3) for same intensity.
(d) Draw this graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I1 > I2 > I3) having same frequency.
A hot body is placed in a closed room maintained at a lower temperature. Is the number of photons in the room increasing?
It is found that photosynthesis starts in certain plants when exposed to sunlight, but it does not start if the plants are exposed only to infrared light. Explain.
Two photons of
Light of wavelength λ falls on a metal with work-function hc/λ0. Photoelectric effect will take place only if
When stopping potential is applied in an experiment on photoelectric effect, no photoelectric is observed. This means that
When the intensity of a light source in increased,
(a) the number of photons emitted by the source in unit time increases
(b) the total energy of the photons emitted per unit time increases
(c) more energetic photons are emitted
(d) faster photons are emitted
Photoelectric effect supports quantum nature of light because
(a) there is a minimum frequency below which no photoelectrons are emitted
(b) the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons depends only on the frequency of light and not on its intensity
(c) even when the metal surface is faintly illuminated the photoelectrons leave the surface immediately
(d) electric charge of the photoelectrons is quantised
The collector plate in an experiment on photoelectric effect is kept vertically above the emitter plate. A light source is put on and a saturation photocurrent is recorded. An electric field is switched on that has a vertically downward direction.
An atom absorbs a photon of wavelength 500 nm and emits another photon of wavelength 700 nm. Find the net energy absorbed by the atom in the process.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A totally reflecting, small plane mirror placed horizontally faces a parallel beam of light, as shown in the figure. The mass of the mirror is 20 g. Assume that there is no absorption in the lens and that 30% of the light emitted by the source goes through the lens. Find the power of the source needed to support the weight of the mirror.
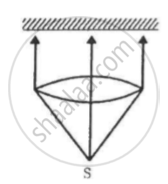
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Find the maximum magnitude of the linear momentum of a photoelectron emitted when a wavelength of 400 nm falls on a metal with work function 2.5 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, the stopping potential is measured for monochromatic light beams corresponding to different wavelengths. The data collected are as follows:-
Wavelength (nm): 350 400 450 500 550
Stopping potential (V): 1.45 1.00 0.66 0.38 0.16
Plot the stopping potential against inverse of wavelength (1/λ) on a graph paper and find (a) Planck's constant (b) the work function of the emitter and (c) the threshold wavelength.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Answer the following question.
Plot a graph of photocurrent versus anode potential for radiation of frequency ν and intensities I1 and I2 (I1 < I2).
In photoelectric effect, the photoelectric current started to flow. This means that the frequency of incident radiations is ______.
In photoelectric effect the photo current ______.
The work function for a metal surface is 4.14 eV. The threshold wavelength for this metal surface is ______.
What is the effect of threshold frequency and stopping potential on increasing the frequency of the incident beam of light? Justify your answer.
