Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The photoelectric cut-off voltage in a certain experiment is 1.5 V. What is the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted?
उत्तर
Photoelectric cut-off voltage, V0 = 1.5 V
The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons is given as:
`"K"_"e" = "eV"_0`
Where,
e = Charge on an electron = 1.6 × 10−19 C
∴ Ke = 1.6 × 10−19 × 1.5
= 2.4 × 10−19 J
Therefore, the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in the given experiment is 2.4 × 10−19 J.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Monochromatic radiation of wavelength 640.2 nm (1 nm = 10−9 m) from a neon lamp irradiates photosensitive material made of caesium on tungsten. The stopping voltage is measured to be 0.54 V. The source is replaced by an iron source and its 427.2 nm line irradiates the same photo-cell. Predict the new stopping voltage.
The work function for the following metals is given:
Na: 2.75 eV; K: 2.30 eV; Mo: 4.17 eV; Ni: 5.15 eV
Which of these metals will not give photoelectric emission for a radiation of wavelength 3300 Å from a He-Cd laser placed 1 m away from the photocell? What happens if the laser is brought nearer and placed 50 cm away?
Is it always true that for two sources of equal intensity, the number of photons emitted in a given time are equal?
It is found that photosynthesis starts in certain plants when exposed to sunlight, but it does not start if the plants are exposed only to infrared light. Explain.
The threshold wavelength of a metal is λ0. Light of wavelength slightly less than λ0 is incident on an insulated plate made of this metal. It is found that photoelectrons are emitted for some time and after that the emission stops. Explain.
When the intensity of a light source in increased,
(a) the number of photons emitted by the source in unit time increases
(b) the total energy of the photons emitted per unit time increases
(c) more energetic photons are emitted
(d) faster photons are emitted
Photoelectric effect supports quantum nature of light because
(a) there is a minimum frequency below which no photoelectrons are emitted
(b) the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons depends only on the frequency of light and not on its intensity
(c) even when the metal surface is faintly illuminated the photoelectrons leave the surface immediately
(d) electric charge of the photoelectrons is quantised
The collector plate in an experiment on photoelectric effect is kept vertically above the emitter plate. A light source is put on and a saturation photocurrent is recorded. An electric field is switched on that has a vertically downward direction.
Calculate the momentum of a photon of light of wavelength 500 nm.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
An atom absorbs a photon of wavelength 500 nm and emits another photon of wavelength 700 nm. Find the net energy absorbed by the atom in the process.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A beam of white light is incident normally on a plane surface absorbing 70% of the light and reflecting the rest. If the incident beam carries 10 W of power, find the force exerted by it on the surface.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A sphere of radius 1.00 cm is placed in the path of a parallel beam of light of large aperture. The intensity of the light is 0.5 W cm−2. If the sphere completely absorbs the radiation falling on it, Show that the force on the sphere due to the light falling on it is the same even if the sphere is not perfectly absorbing.
Define the term: threshold frequency
Explain how does (i) photoelectric current and (ii) kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in a photocell vary if the frequency of incident radiation is doubled, but keeping the intensity same?
Show the graphical variation in the above two cases.
In photoelectric effect, the photoelectric current started to flow. This means that the frequency of incident radiations is ______.
Consider a metal exposed to light of wavelength 600 nm. The maximum energy of the electron doubles when light of wavelength 400 nm is used. Find the work function in eV.
If photons of ultraviolet light of energy 12 eV are incident on a metal surface of work function of 4 eV, then the stopping potential (in eV) will be :
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
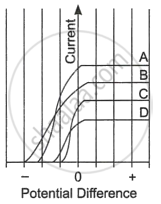
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
How would the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface change if the frequency of the incident radiation were increased? Justify your answer.
