Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Photoelectric effect supports quantum nature of light because
(a) there is a minimum frequency below which no photoelectrons are emitted
(b) the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons depends only on the frequency of light and not on its intensity
(c) even when the metal surface is faintly illuminated the photoelectrons leave the surface immediately
(d) electric charge of the photoelectrons is quantised
Solution
(a) there is a minimum frequency below which no photoelectrons are emitted
(b) the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons depends only on the frequency of light and not on its intensity
(c) even when the metal surface is faintly illuminated the photoelectrons leave the surface immediately
Photoelectric effect can be explained on the basis of quantum nature of light. According to the quantum nature of light, energy in light is not uniformly spread. It is contained in packets or quanta known as photons.
Energy of a photon, E = hv, where h is Planck's constant and v is the frequency of light.
Above a particular frequency, called threshold frequency, energy of a photon is sufficient to emit an electron from the metal surface and below which, no photoelectron is emitted, as the energy of the photon is low. Hence, option (a) supports the quantum nature of light.
Now, kinetic energy of an electron,
`K = hv_0 - varphi`
Thus, kinetic energy of a photoelectron depends only on the frequency of light (or energy). This shows that if the intensity of light is increased, it only increases the number of photons and not the energy of photons. Kinetic energy of photons can be increased by increasing the frequency of light or by increasing the energy of photon, which supports E = hv and, hence, the quantum nature of light. Hence, option (b) also supports the quantum nature of light.
Photoelectrons are emitted from a metal surface even if the metal surface is faintly illuminated; it means that less photons will interact with the electrons. However, few electrons absorb energy from the incident photons and come out from the metal. This shows the quantum nature of light. Hence, (c) also supports the quantum nature of light.
Electric charge of the photoelectrons is quantised; but this statement does not support the quantum nature of light.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw graphs showing variation of photoelectric current with applied voltage for two incident radiations of equal frequency and different intensities. Mark the graph for the radiation of higher intensity.
A hot body is placed in a closed room maintained at a lower temperature. Is the number of photons in the room increasing?
If an electron has a wavelength, does it also have a colour?
Let nr and nb be the number of photons emitted by a red bulb and a blue bulb, respectively, of equal power in a given time.
The work function of a metal is hv0. Light of frequency v falls on this metal. Photoelectric effect will take place only if
If the frequency of light in a photoelectric experiment is doubled, the stopping potential will ______.
A point source of light is used in a photoelectric effect. If the source is removed farther from the emitting metal, the stopping potential
In which of the following situations, the heavier of the two particles has smaller de Broglie wavelength? The two particles
(a) move with the same speed
(b) move with the same linear momentum
(c) move with the same kinetic energy
(d) have fallen through the same height
Calculate the number of photons emitted per second by a 10 W sodium vapour lamp. Assume that 60% of the consumed energy is converted into light. Wavelength of sodium light = 590 nm
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A totally reflecting, small plane mirror placed horizontally faces a parallel beam of light, as shown in the figure. The mass of the mirror is 20 g. Assume that there is no absorption in the lens and that 30% of the light emitted by the source goes through the lens. Find the power of the source needed to support the weight of the mirror.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Find the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons ejected when light of wavelength 350 nm is incident on a cesium surface. Work function of cesium = 1.9 eV
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The work function of a metal is 2.5 × 10−19 J. (a) Find the threshold frequency for photoelectric emission. (b) If the metal is exposed to a light beam of frequency 6.0 × 1014 Hz, what will be the stopping potential?
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The work function of a photoelectric material is 4.0 eV. (a) What is the threshold wavelength? (b) Find the wavelength of light for which the stopping potential is 2.5 V.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Find the maximum magnitude of the linear momentum of a photoelectron emitted when a wavelength of 400 nm falls on a metal with work function 2.5 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
In the case of photoelectric effect experiment, explain the following facts, giving reasons.
The photoelectric current increases with increase of intensity of incident light.
Define the term: stopping potential in the photoelectric effect.
Explain how does (i) photoelectric current and (ii) kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in a photocell vary if the frequency of incident radiation is doubled, but keeping the intensity same?
Show the graphical variation in the above two cases.
If photons of ultraviolet light of energy 12 eV are incident on a metal surface of work function of 4 eV, then the stopping potential (in eV) will be :
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
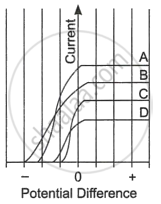
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
