Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find the maximum magnitude of the linear momentum of a photoelectron emitted when a wavelength of 400 nm falls on a metal with work function 2.5 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Solution
Given :-
wavelength of light , `λ = 400 "nm" = 400 xx 10^-9 "m"`
Work function of metal, `phi = 2.5 "eV"`
From Einstein's photoelectric equation,
Kinetic energy = `(hc)/λ - phi`
Here, c = speed of light
h = Planck's constant
`therefore K.E. = (6.63 xx 10^-34 xx 3 xx 10^8)/(4 xx 10^-7 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19) - 2.5 "eV"`
`= 0.605 "eV"`
Also , `K.E. = p^2/(2m)`
where p is momentum and m is the mass of an electron.
`therefore p^2 = 2"m" xx K.E.`
`⇒ p^2 = 2 xx 9.1 xx 10^-31 xx 0.605 xx 1.6 xx 10^-19`
`⇒ p = 4.197 xx 10^-25 "kg - m/s"`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The following graph shows the variation of photocurrent for a photosensitive metal :
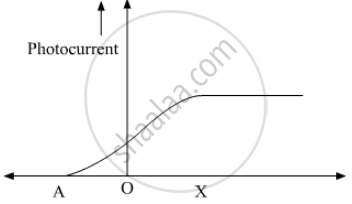
(a) Identify the variable X on the horizontal axis.
(b) What does the point A on the horizontal axis represent?
(c) Draw this graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation v1, v2 and v3 (v1 > v2 > v3) for same intensity.
(d) Draw this graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I1 > I2 > I3) having same frequency.
What is the speed of a photon with respect to another photon if (a) the two photons are going in the same direction and (b) they are going in opposite directions?
In an experiment on photoelectric effect, a photon is incident on an electron from one direction and the photoelectron is emitted almost in the opposite direction. Does this violate the principle of conservation of momentum?
The equation E = pc is valid
The work function of a metal is hv0. Light of frequency v falls on this metal. Photoelectric effect will take place only if
Light of wavelength λ falls on a metal with work-function hc/λ0. Photoelectric effect will take place only if
When the intensity of a light source in increased,
(a) the number of photons emitted by the source in unit time increases
(b) the total energy of the photons emitted per unit time increases
(c) more energetic photons are emitted
(d) faster photons are emitted
In which of the following situations, the heavier of the two particles has smaller de Broglie wavelength? The two particles
(a) move with the same speed
(b) move with the same linear momentum
(c) move with the same kinetic energy
(d) have fallen through the same height
A 100 W light bulb is placed at the centre of a spherical chamber of radius 20 cm. Assume that 60% of the energy supplied to the bulb is converted into light and that the surface of the chamber is perfectly absorbing. Find the pressure exerted by the light on the surface of the chamber.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
A sphere of radius 1.00 cm is placed in the path of a parallel beam of light of large aperture. The intensity of the light is 0.5 W cm−2. If the sphere completely absorbs the radiation falling on it, Show that the force on the sphere due to the light falling on it is the same even if the sphere is not perfectly absorbing.
The electric field associated with a light wave is given by `E = E_0 sin [(1.57 xx 10^7 "m"^-1)(x - ct)]`. Find the stopping potential when this light is used in an experiment on photoelectric effect with the emitter having work function 1.9 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
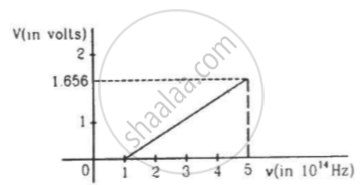
The figure is the plot of stopping potential versus the frequency of the light used in an experiment on photoelectric effect. Find (a) the ratio h/e and (b) the work function.

On the basis of the graphs shown in the figure, answer the following questions :
(a) Which physical parameter is kept constant for the three curves?
(b) Which is the highest frequency among v1, v2, and v3?
In the case of photoelectric effect experiment, explain the following facts, giving reasons.
The photoelectric current increases with increase of intensity of incident light.
In photoelectric effect the photo current ______.
Consider a 20 W bulb emitting light of wavelength 5000 Å and shining on a metal surface kept at a distance 2 m. Assume that the metal surface has work function of 2 eV and that each atom on the metal surface can be treated as a circular disk of radius 1.5 Å.
- Estimate no. of photons emitted by the bulb per second. [Assume no other losses]
- Will there be photoelectric emission?
- How much time would be required by the atomic disk to receive energy equal to work function (2 eV)?
- How many photons would atomic disk receive within time duration calculated in (iii) above?
- Can you explain how photoelectric effect was observed instantaneously?
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
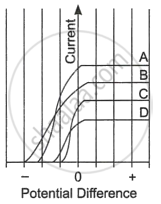
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
A metallic plate exposed to white light emits electrons. For which of the following colours of light, the stopping potential will be maximum?
What is the effect of threshold frequency and stopping potential on increasing the frequency of the incident beam of light? Justify your answer.
